Who are the leading innovators in Byzantine Fault Tolerant Blockchain for the Technology Industry?
[gpt3]rewrite
The technology industry continues to be a hotbed of innovation, with activity driven by the need for stronger and more comprehensive cybersecurity measures to protect against cyber threats and attacks, as well as the growing importance of technologies such as Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), Federated Byzantine Agreement (FBA), Byzantine fault-tolerant replication (BFT-R), and practical Byzantine fault-tolerant with state machine replication (PBFT-SMR). These technologies and consensus algorithms contribute to the development of Byzantine fault-tolerant blockchains, ensuring the system’s resilience against malicious or erroneous behavior. In the past three years alone, there have been over 3.6 million patents filed and granted in the technology industry, according to GlobalData’s Innovation in Cybersecurity: Byzantine Fault Tolerant Blockchain report.
However, not all innovations are equal, nor do they follow a constantly upward trend. Instead, their development takes the form of an S-shaped curve that reflects their typical life cycle from early emergence to accelerating adoption, before finally stabilizing and reaching maturity.
Identifying where a particular innovation is on this journey, especially those in emerging and accelerating stages, is critical to understanding their current level of adoption and the likely future trajectory and impact they will have.
300+ innovations will shape the technology industry
According to GlobalData’s Technology Foresights, which plots the S-curve of the technology industry using innovation intensity models built on over 2.5 million patents, there are 300+ areas of innovation that will shape the future of the industry.
Within shows up innovation stage, Byzantine fault tolerant blockchain, secure multiparty computing and decentralized identity framework are disruptive technologies that are in the early stages of application and should be closely tracked. Secure hash algorithms (SHA), zero knowledge secure and private blockchains are some of these accelerating innovation areas, where adoption has been steadily increasing. Among matures areas of innovation are firmware security, multimedia signal encryption and biometric authentication, which are now well established in the industry.
Innovation S-curve for cyber security in the technology industry
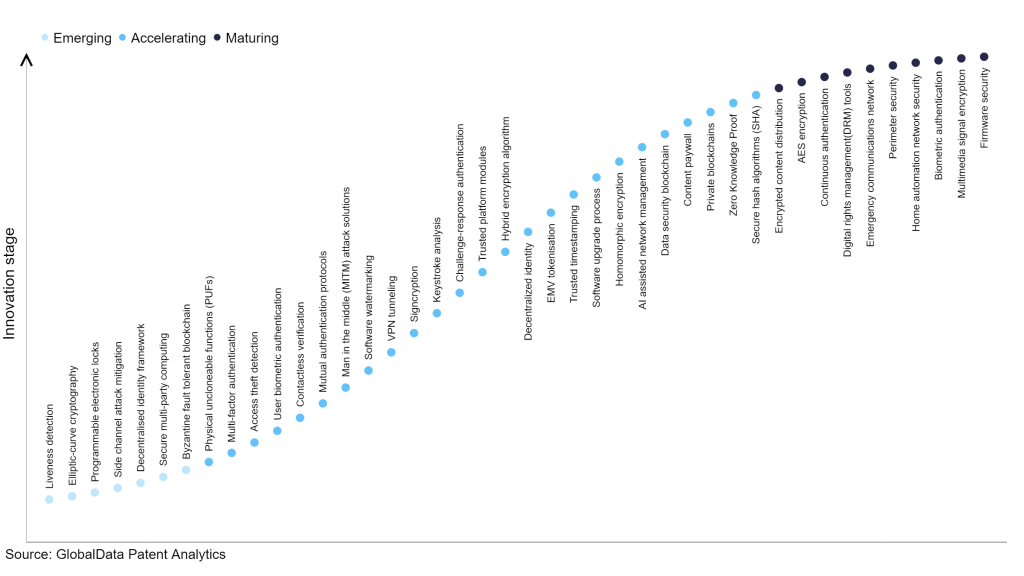
Byzantine fault-tolerant blockchain is a key area of innovation in cyber security
Byzantine fault-tolerant blockchain refers to a form of distributed ledger technology capable of establishing consensus in the face of malicious participants. The name is derived from the Byzantine Generals Problem, an influential computer science problem originally outlined in 1982. By using consensus algorithms, this technology guarantees the prevention of disturbances caused by malicious actors, thus ensuring the successful achievement of consensus in the system.
GlobalData’s analysis also uncovers the companies at the forefront of each area of innovation and assesses the potential reach and impact of their patenting activity across different applications and geographies. According to GlobalData, there are 40+ companies, spanning technology vendors, established technology companies, and new startups that are engaged in the development and use of Byzantine fault-tolerant blockchain.
Key players in Byzantine fault-tolerant blockchain – a disruptive innovation in the technology industry
“Application diversity” measures the number of different applications identified for each relevant patent, dividing companies into either “niche” or “diversified” innovators.
“Geographical scope” refers to the number of different countries each relevant patent is registered in, and reflects the breadth of geographic application intended, from “global” to “local.”
Patent volumes related to Byzantine fault-tolerant blockchain
Source: GlobalData Patent Analytics
SoftBank Group is one of the leading patent applicants in Byzantine fault-tolerant blockchain. The company’s patents are directed to implementations of this specification, including a computer-implemented method for achieving consensus among multiple network nodes in a blockchain network. The blockchain network includes a primary node and one or more backup nodes.
The method includes receiving a transaction request from the primary node, sending multiple first messages to the backup nodes of the primary node, receiving second messages from the backup nodes of the primary node, reconstructing the transaction request based on data in the other messages from the primary node, sending a third message to the backup nodes of the primary node, and executing the transaction request in response to receiving a predetermined number of third messages.
Other prominent patent applicants in the area include International Business Machines (IBM) and Tencent.
In terms of geographic reach, SICPA leads the pack, followed by Everseen and Furukawa. In terms of application diversity, Vanguard Group holds the top position, followed by SICPA and nChain.
Byzantine fault-tolerant blockchain provides a robust and secure consensus mechanism even in the presence of malicious actors. It secures against various attack vectors, including node failures, network partitions, and intentional malicious behavior, thereby maintaining the integrity of the blockchain network.
To further understand how cybersecurity is disrupting the technology industry, access GlobalData’s latest thematic research report on Cybersecurity – Thematic Research.
[gpt3]



