What is Carbon Offsetting in Blockchain Technology?
You’ve probably heard that blockchain technology, especially the one Bitcoin uses, has a detrimental environmental impact on the world. This is because mining can release large amounts of carbon, which can harm the global environment.
However, several organizations have started using blockchain technology to cancel these emissions in what is called carbon offset. So what is carbon offsetting using blockchain technology and can it really help the environment?
Carbon offsetting using blockchain technology explained
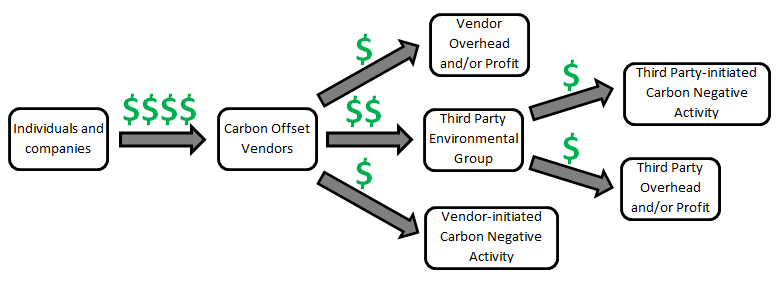
Carbon offsetting involves buying carbon credits to offset your carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions; one carbon credit offsets one metric tonne of carbon dioxide. The organization that sells you carbon credits usually uses the money you pay to fund actions that remove the same amount of carbon dioxide as you emit, such as capturing methane gas, building solar or wind farms, and conserving forests.
You become carbon neutral when your carbon credit equals your carbon footprint – the amount of carbon dioxide you emit.
In the 1990s, faced with the evidence of the threat of climate change, the United Nations launched the Kyoto Protocol, the international treaty that introduced carbon credits to reduce CO2 emissions. This treaty led to the emergence of the carbon market, enabling governments, businesses and other legal parties to limit carbon dioxide emissions.
But while several international agencies regulate carbon credit registrations and sales, a largely unregulated voluntary carbon market exists. Participants in this voluntary market seek to compensate for their emissions beyond the imposed requirements. This is where blockchain technology comes in.
The carbon market can become more transparent and easily accessible with the help of blockchain technology. However, some organizations have been known to offer carbon credits that do not fund carbon reduction measures, and some voluntary market participants have made false claims about their carbon neutrality.
Suppose the voluntary carbon market is placed on a blockchain. In that case, each carbon credit will have metadata proving its origin and quality, offering a transparent, affordable and highly liquid carbon compensation market. Also, regulatory agencies can better assess claims of carbon neutrality.
Blockchain technology can reduce costs, help avoid double consumption, reduce paperwork and make the carbon market more efficient. But blockchains are programmed, so they only work according to the information they are fed. They cannot distinguish between good and bad credit data. However, combined with a central carbon credit agency, blockchain technology can help monitor and verify carbon credit-related data so that the disadvantages of the voluntary market are avoided.
Although some critics say that carbon credits allow organizations to emit carbon guilt-free, others insist that carbon offsets can finance sustainable development projects to reduce CO2 emissions if done correctly.
How does carbon offsetting work with blockchain technology?
The first step in carbon offsetting is to calculate your carbon emissions. Calculating your carbon footprints regularly and including them in your financial and sustainability reports is good practice, as more countries require emissions reporting. For example, companies in the USA must report annual emissions of over 25,000 tonnes of CO2. You can use protocols like the GHG Protocol to measure and manage your CO2 emissions – usually with a sustainability strategy.
Although you can reduce CO2 emissions by using small actions, such as switching to greener transport, you will probably have to offset a good portion of your emissions. And for you to offset your carbon footprint, you need to use a project certified to issue carbon credits, such as the Climate Action Reserve. However, with blockchain technology, the carbon credits will be created and issued digitally, along with proof that you have purchased carbon credits.
Smart contracts on the blockchain can store metadata about carbon credits and convert them into tradable units, enabling fast, transparent and reliable information exchange between network participants. These features can be used to buy carbon credits to improve the carbon market.
3 Examples of blockchain-based suppliers of carbon solutions
Gold Standard, a certified carbon credit issuer, is intended to symbolize carbon credits. However, several blockchains exist that issue digital carbon credits, albeit uncertified. But their credits represent permanent reductions or removals of carbon emissions and do not cause carbon emissions elsewhere.
These are a few blockchain-based carbon credit issuers.
1. Climate trading
ClimateTrade uses blockchain technology, in accordance with a verified carbon standard, to enable individuals and companies to offset their carbon emissions in a transparent manner. Every carbon credit transaction is made visible to everyone on the ClimateTrade system. And the platform claims that the UN recognizes it and that it verifies all the carbon projects in its portfolio.
With a ClimateTrade account, you can access and manage all your carbon credit transactions. You can also integrate the ClimateTrade API and Widget into your platform, so that your products and services become climate positive.
2. CarbonX
This software fintech creates investments for carbon offsetting projects through the Carbon X Hub, a private blockchain (different from a public blockchain) that captures carbon emissions data for measurement, management and reporting.
As a result of CarbonX’s partnership with Zerofootprint in 2019, the platform can calculate the carbon associated with your products and services and determine the appropriate amount of carbon offset. You can set carbon neutrality goals and receive a Zero Footprint certificate when you reach them.
CarbonX claims to have been recognized by Barack Obama, the Government of Ontario and the Clinton Foundation.
3. IMPT
IMPT was developed to help everyone fight climate change. The platform connects individuals and organizations with verified carbon offsetting projects.
You can trade with a variety of brands, including Samsung, AliExpress and Nike, via IMPT to earn IMPT tokens. These tokens can be converted into carbon credits, which help reduce global carbon levels. Alternatively, you can buy carbon credits at IMPT to reduce your carbon footprint.
With an IMPT account you can manage your carbon credits – you can burn, sell or keep your credits. The platform also offers an IMPT program, which allows you to earn points and exchange them for carbon credits. Additionally, you can burn your carbon credits to receive a collectible non-fungible token (NFT) that can be traded on several of the top NFT marketplaces.
Blockchain technology can fight climate change
Carbon compensation can mitigate climate change, but the space – especially the voluntary market – requires better frameworks. Blockchain technology is a good solution to the core problems of carbon markets, as it can offer greater transparency and trust.
Although still a new concept, several applications indicate that carbon offsetting using blockchain technology will be crucial in the future. The challenge is for regulatory bodies to agree on blockchain standards so that only good data is entered, which ensures integrity in the chain. These bodies must decide how digital carbon credits are created, how they are given value, what they represent and other relevant details.