What are crypto price gaps and how can you spot them?
Price gaps occur in all financial markets and are evident in candlestick patterns and price bars. How these gaps occur determines their interpretation and what traders expect from them. If you trade crypto constantly, you must have noticed these gaps, especially in smaller time frames. Knowing what price gaps are and how they occur and are interpreted will benefit your crypto trading strategy.
What is a price gap?
If you study candlestick charts regularly, you will notice that there are sometimes visible gaps between two candlesticks or the end of one candlestick and the opening price of the next – these are price gaps.
A price gap is a phenomenon that occurs when the price of a cryptocurrency jumps from one price to another. When a price gap occurs, no trade takes place at the jump price, resulting in a visible unfilled space. Price gaps occur in both bearish and bullish markets.
A price gap and a slide are similar since they are both characterized by sharp changes in price; however, they are different. A slippage causes a difference between the price you wish to execute a trade and the actual execution price. It is also caused by a sharp price movement, which is not necessarily a gap.
Why do crypto price gaps happen?
Price gaps in cryptocurrency occur for two main reasons: price volatility and illiquidity.
Many factors cause the market price to experience an increase in volatility. These factors range from news reports of major market events and happenings to the activities of major players and influencers, which can cause a significant change in market sentiment.
Exchanges and cryptocurrencies can also experience illiquidity due to factors such as a lack of market makers and low trading volume. Illiquidity can cause the price to be unstable, thus causing a price gap.
Market manipulation techniques such as wash trading and pump-and-dump schemes can also cause price gaps as they tend to increase price volatility, especially when trading a fraudulent exchange or a cryptocurrency that is prone to manipulation.
Price gaps are more common in financial markets with a specific closing time. For example, currency markets close on weekends. However, major events that will not be visible on the price chart may occur during the closing period. For this reason, it is common to see the price open at a different price at the beginning of the week than it closed on Friday.
4 Types of Crypto Price Gaps and How to Identify Them
The following are types of crypto price gaps based on price action.
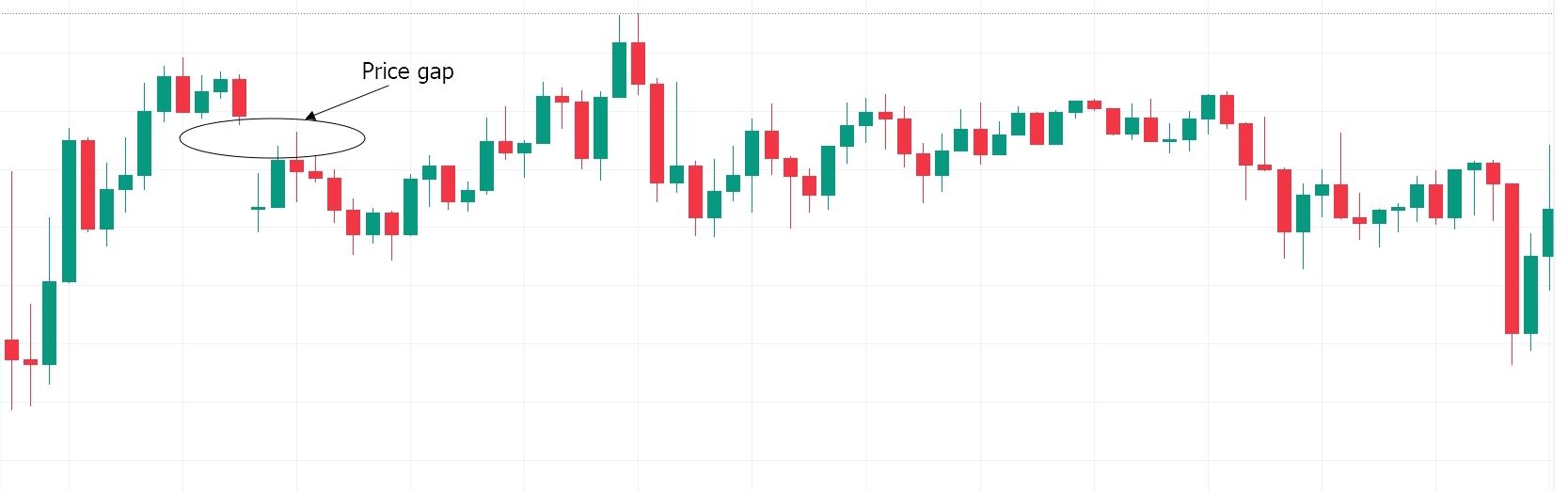
1. Common gap
Normal gaps are random gaps that occur without regard to any particular price action. As the name suggests, they are common and are triggered under normal market conditions. Common gaps can be upward or downward and may not provide specific trading signals.
The common gap in the chart above occurred when price had no specific direction. The price returned to fill the gap almost immediately, after which the price continued its random movement.
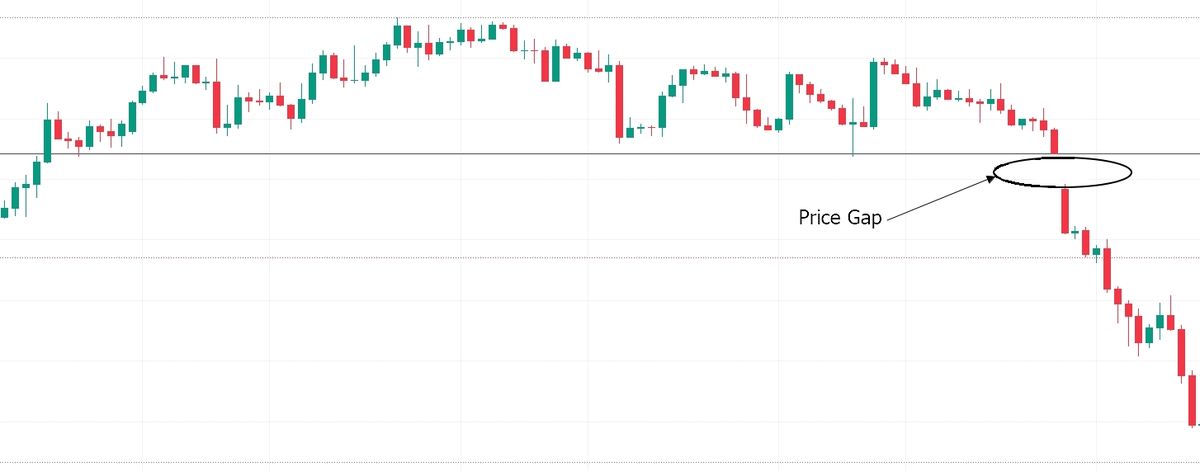
2. Breakaway Gap
A breakaway gap breaks major support or resistance and usually signals the beginning of a trend. You will notice this type of price gap when price breaks out of a fluctuating market. If the price gap breaks the support, the price may continue downward. However, if it breaks the price resistance, the price may continue to rise.
The chart above shows a breakout gap that broke through a price support level. After that, the price continued to fall. In this example, the breakaway gap signaled the start of a bearish trend.
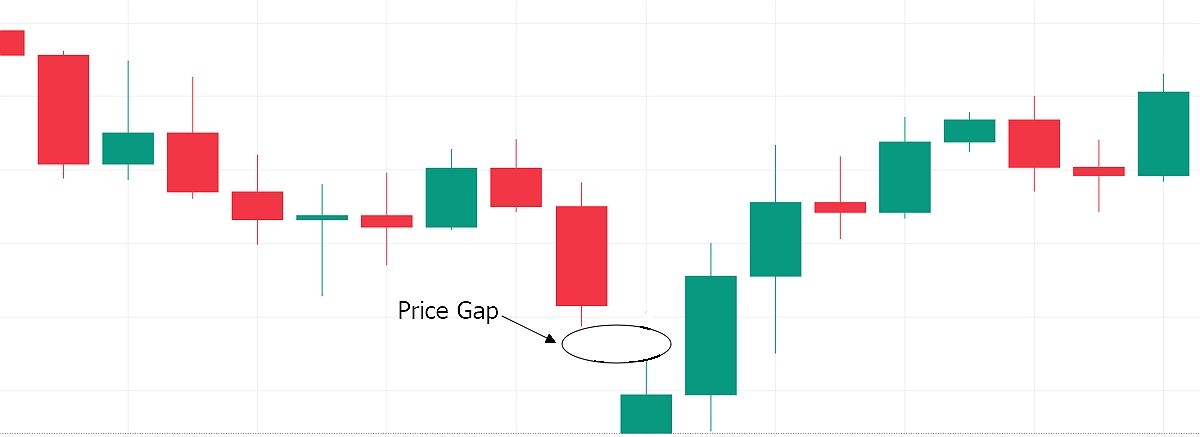
3. Exhaustion gap
An exhaustion gap signals the end of a trend. It is characterized by a price gap against the direction of the trend before the price reverses. The gap can be a sharp move up followed by a bearish reversal in a bullish trend and reverse in a bearish trend.
In the chart above, the exhaustion gap showed the end of the downward price movement. The price started to move upwards immediately after the gap.
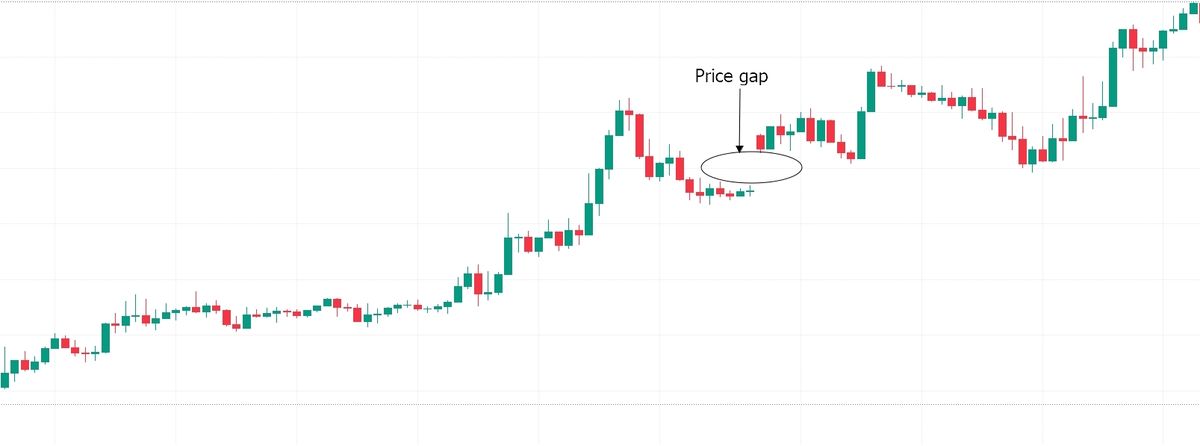
4. Continuation gap
A continuation gap occurs during a bullish or bearish trend to show that the trend is likely to continue. For example, if a continuation gap occurs in an uptrend, it shows that the trend is likely to continue upward, and if it is in a downtrend, it is likely to continue downward.
In the chart above, the continuation gap occurred during a minor price reduction within a strong uptrend. The appearance signaled strong buying action, showing the end of the price correction and the continuation of the main trend.
Can crypto traders take advantage of price gaps?
Traders generally believe that gaps are usually filled, and when a price gap occurs, they expect the price to move back at some point to fill the gap.
As much as this is true to some extent, it happens more with some price gaps than others. For example, exhaustion and breakout gaps are trend-changing price gaps. Thus, the likelihood of price going back to fill the gaps may be minimal.
To make the most of the price gap and know what function the price gap performs, traders may need to wait for the number of candlesticks to close. For example, you may not be able to tell if a candlestick is really an exhaustion gap until you see that the price has started to move in the opposite direction. The number of candlesticks that close the gap faster will determine how you approach the market.
You cannot trade price gaps alone
When trying to take advantage of price gaps, traders study price action to find the best way to profit from the market movement. However, price gaps usually do not include all the information needed to execute trades.
For example, holes usually do not provide clear entry and exit points. You need to use other tools and indicators to determine where your trade entry, take-profit and stop-loss prices should be.
Price gaps do not occur regularly in many crypto markets. Thus, basing your strategy on price gaps may mean that you will not get trade entry signals often, especially if you are trying to trade popular cryptocurrencies. The better option is to trade price gaps as part of a broader crypto strategy rather than making it your main strategy.