Top 9 blockchain platforms to consider in 2022
Interest in blockchain platforms has increased significantly as a way to streamline supply chains, improve traceability, simplify trading and improve financial transactions. Much of this interest started with the speculative madness surrounding Bitcoin, which is based on an older blockchain platform that faces challenges with energy consumption and speed.
Modern blockchain platforms are designed to help overcome these limitations and provide practical value for other business uses and applications. “We see more companies using blockchain platforms for some of their application needs,” said Suseel Menon, senior analyst at Everest Group, an IT consulting firm.
Menon is most interested in areas that require multi-party collaboration or data exchange. Blockchain applications in supply chain tracking, trade finance, digital assets and identity management go beyond the pilot stage. Menon also sees some activity in using blockchain platforms to build certain functions in ERP, such as supplier management and supply chain management (SCM).
Alex-Paul Manders, partner at Information Services Group, an IT consulting firm, said that the development of blockchain platforms to date has raised awareness of decentralized finance, or DeFi, to drive new business models that pose significant threats to traditional banking. finance and supply chain financing.
 Alex-Paul Manders
Alex-Paul Manders
Manders predicted that blockchain platforms could disrupt older supply chain companies and technological processes. For example, US requirements for pharmaceutical companies to track and track products and materials require a new approach for supply chain participants to share and transact data more efficiently and with more transparency than previously necessary. Blockchain technology may be the answer.
According to Menon, the three best blockchain frames for these use cases are R3 Corda, Hyperledger and Ethereum, with EOSIO and Quorum gaining ground.
Here are nine of the best blockchain platforms to consider.
 Suseel Menon
Suseel Menon
1. Ethereum
Ethereum was introduced in 2013 and is one of the oldest and most established blockchain platforms. It provides a truly decentralized blockchain that is comparable to the Bitcoin blockchain network. Manders said that its most important strength is that it enables real decentralization with the support of smart contracts. Its main weaknesses include slow processing times and higher transaction processing costs compared to other platforms. In addition to its role as a blockchain platform that supports enterprise applications, it has its own cryptocurrency called ether.
The Ethereum platform sees widespread use of technologies that build decentralized applications, or dApps, on the Ethereum network. For example, there are many platforms and exchanges for non-fungible tokens (NFT) – a type of digital asset that can be exchanged on a blockchain. It has a mature ecosystem of tools for writing smart contracts using the Solidity programming environment, which runs on the Ethereum Virtual Machine. However, alternative blockchain networks can process transactions much faster at potentially lower costs than Ethereum, although many observers expect this to change after Ethereum adopts a more efficient security mechanism.
It also has an active developer community orchestrated by the Enterprise Ethereum Alliance, which has more than 250 members, including Intel, JPMorgan and Microsoft.
The Ethereum community is migrating from the existing proof of work (PoW) consensus mechanism to proof of stake (PoS), which is more energy friendly. This migration has required an elaborate process to spin up a separate, new type of blockchain called a Beacon chain that is merged into the existing Ethereum blockchain. The Ethereum Foundation estimates that this will reduce energy consumption by 99.95%.
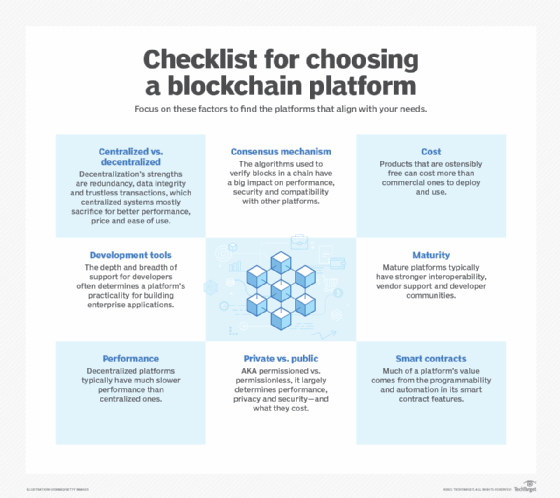
2. IBM Blockchain
IBM Blockchain is a private, decentralized blockchain network that has been most successful with corporate customers who are less risk-averse, Manders said. He sees the greatest potential in using it to connect to enterprise cloud and older technologies more seamlessly than is possible in other decentralized networks.
The IBM Blockchain Developer Tool was designed to be flexible, functional and customizable. IBM has also invested in creating a user-friendly interface to simplify critical tasks, such as setting up, testing and quickly implementing smart contracts.
 Rakesh Mohan
Rakesh Mohan
Rakesh Mohan, IBM’s director of blockchain solutions development, said the company has seen significant progress in financial services and banking, as well as the supply chain. Some examples of successful blockchain apps include the IBM Food Trust, which has completed more than 18 million transactions representing more than 17,000 products, and the Blockchain Community Initiative in Thailand, which supports services such as payment obligations and corporate auctions for 22 Thai banks.
3. Hyperledger fabric
Hyperledger Fabric is a set of tools that help create blockchain applications. It was championed by The Linux Foundation, and was built from the ground up for distributed ledger use. It has a rich ecosystem of components that can be connected to a modular architecture. It works well in closed blockchain distributions, which can improve security and speed. It also supports an open smart contract model that can support various data models, such as account and unused transaction output, or UTXO models (see sidebar).
Hyperledger Fabric can also improve data privacy by isolating transactions in channels or enabling the sharing of private data as needed in private data collections. It also enables high-speed transactions with low latency for finality and confirmation, according to its spokesmen.
Arnaud Le Hors, senior technical associate in blockchain and web-open technologies at IBM, who is also a member of the Hyperledger Technical Steering Committee, said that the latest developments support an organization to join a channel without copying the entire history of the general ledger . This enables a faster start-up process with less storage requirements. There is an active and diverse community around Hyperledger Fabric working to add more features related to consensus algorithms, additional privacy options for GDPR compliance and operational improvements.
4. Hyperledger Sawtooth
Another open source blockchain initiative hosted by Hyperledger and The Linux Foundation, Hyperledger Sawtooth uses a new consensus mechanism called time-lapse proof that can be integrated with hardware-based security technologies to enable “reliable execution environments” of program code to run in secure enclaves, such as are protected areas of computer memory.
 Shawn Amundson
Shawn Amundson
Shawn Amundson, CTO of Bitwise IO and Hyperledger Sawtooth maintainer, said the most common applications are for developing supply chain systems and customizing Sawtooth for specific purposes, such as new consensus algorithms.
Work has begun on a Sawtooth library that will allow developers of custom distributed ledgers to select and reject which parts of Sawtooth they use in the application. At the same time, Sawtooth uses Splinter for networking, which will provide dynamic private circuits (groups of nodes); Hyperledger Transact for transaction processing, which will expand smart contract options; and Augrim for Consensus, which will expand the number of supported algorithms.
5. R3 Corda
There is some debate as to whether R3 Corda is technically a blockchain or an alternative type of distributed ledger. It uses a new consensus mechanism where transactions are cryptographically linked, but do not periodically group several transactions in a block. Even the official Corda website describes it as “both a blockchain and not a blockchain.” One of the key benefits of this approach is that all transactions are processed in real time, which can improve performance compared to other types of blockchains.
The R3 consortium has a strong following in the financial industry, since Corda provides an attractive approach for financial transactions and smart contracts with strong security. Leading spokesmen include Bank of America, HSBC, Intel and Microsoft. It supports tools that automate business logic that can be executed across business boundaries. The group has also recently launched a technical preview of Corda Payments, which simplifies the process of building distributed payment options into apps.
Manders said that Corda has a strong chance to become the de facto network for insurance-related transaction processing. However, it faces competition from other unified blockchain networks that can process transactions faster and cheaper.
6. Tezos
In development since 2014, Tezos is an older platform that supports decentralized applications, smart contracts and new financial instruments, such as NFTs, which can be thought of as a modern variant of trading cards linked to digital assets. The platform supports a dynamically upgradeable protocol and modular software clients that enable it to adapt to new applications. The Tezos community has upgraded the platform in a quick cut, with recent improvements that have improved performance and increased the size limit of smart contracts. It has also developed tools to automate the process of weaving NFTs into your company’s supply chains.
7. EOSIO
The EOSIO blockchain platform was first launched as an open source project in 2018. It is optimized for the development of decentralized applications and smart contracts. It uses a complex consensus mechanism based on PoS that provides better performance than older mechanisms, such as Ethereum, according to spokesmen. It also includes support for a management function to vote on changes to the platform.
Key strengths include fast transactions and advanced account licensing features for deploying applications. Over 400 applications have been developed on the platform, including identity management, SCM and games. The community also offers various tools for customizing blockchain implementations for various decentralized use cases in SCM, healthcare and DeFi.
8. Stellar
Stellar is a newer blockchain platform optimized for different types of DeFi applications. It uses the Stellar Consensus Protocol, which reportedly can increase the time required to process and complete transactions on a public blockchain network. It also includes security mechanisms to exclude bad or questionable players in a financial transaction. Several companies have been used for international trade and exchange of money across national borders. Examples of applications built on the Stellar blockchain include MoneyGram for money transfer, Circle for payments and financial infrastructure, and Flutterwave for integrating payment processing into enterprise applications.
9. ConsenSys Quorum
Quorum is a customized version of Ethereum developed by the finance company JPMorgan. It takes advantage of the core work on the Ethereum blockchain platform and repackages it into a hardened environment suitable for banks. It has been optimized to support high-speed transactions between institutions such as banks and insurance companies on a private network. It also adds various privacy enhancements to Ethereum to improve support for regulations such as the GDPR in Europe and the CCPA in California.
ConsenSys acquired the Quorum platform’s intangible assets from JPMorgan at the end of 2021 and integrated these into its own work to create the ConsenSys Quorum open source protocol layer. ConsenSys has positioned this offering as a way for businesses to accelerate the development of enterprise applications that complement other Ethereum-based tools. The company provides development services for the combined platform to corporate clients, including JPMorgan and South African Reserve Bank.


