North Korean hackers use cloud computing to launder crypto
North Korea-based hackers are increasingly using cryptocurrencies to facilitate illegal activities. According to the latest study, the hacker group is using it to mine more crypto via cloud services.
Cryptocurrency and the underlying blockchain technology have demonstrated various applications over the years. One of the unfortunate routes that emerged was a new way of financing espionage operations. Espionage is the act of spying on others for political, military or economic gain.
Cryptocurrencies offer a level of anonymity and decentralization that traditional forms of finance cannot match. These features make it difficult for authorities to trace the source of funds used to finance espionage activities.
How does cryptocurrency play a role here?
Unfortunately, hackers have used various crypto services to launder stolen currency. Hackers use crypto services such as exchanges, wallets and mingling services to hide the origin of their stolen funds.
Anonymity: Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum are decentralized. They do not rely on a central authority to verify transactions. This anonymity makes it difficult for authorities to trace the flow of money, which is why it has become an attractive option for financing espionage activities. The use of pseudonyms and encrypted messages also makes it difficult to trace the source of the transactions.
Decentralization: Traditional forms of financing require a bank or other financial institution to process transactions. On the other hand, cryptocurrencies are decentralized. Two parties can send and receive funds directly without a third party confirming the transaction. Decentralization makes it difficult for governments to freeze or seize funds for espionage activities.
Lack of regulations: Many countries have no clear rules around cryptocurrencies. This makes it easier for spies to use them to finance their operations. Consequently, there are no restrictions on how much money is transferred, where the funds are sent or who uses them.
Other features to consider
Difficulty tracking: A public ledger called blockchain records cryptocurrency transactions. The identity of the parties involved is unknown. This makes it difficult for law enforcement agencies to trace the source of funds used to finance espionage activities.
Cryptocurrency mixers: Cryptocurrency mixers are services that allow users to mix their coins with other users’ coins to make it difficult to trace the source of the funds. These services are popular with criminals and spies because they provide an extra layer of anonymity.
Lack of paper trail: Cryptocurrency transactions do not leave a paper trail, making it difficult for law enforcement agencies to trace the funds back to their source. Traditional forms of financing such as bank transfers or checks leave a paper trail that can be followed. Cryptocurrency transactions are more difficult to trace.
Speed and efficiency: Cryptocurrency transactions are fast and efficient and complete in minutes. This speed and efficiency makes it easier for spies to transfer money quickly and efficiently without attracting too much attention.
Most of the notorious hackers come from North Korea
North Korean hackers have been operating in the cryptosphere for several years now. North Korea is without a doubt one of the most active state actors in cybercrime. The hackers have carried out high-profile attacks on cryptocurrency exchanges, wallets and protocols. One such collective is the infamous Lazarus Group.
The latest report from Google-owned cybersecurity firm Mandiant focused on a North Korean threat group called APT43. This group primarily targets the technology, healthcare and aerospace industries, funded by cryptocurrencies.
Although its main activity is spying on South Korea, Mandiant found that APT43 likely raised money for the North Korean regime and financed itself through its illegal operations. The group has been successful in these jobs:
“APT43 steals and launders enough cryptocurrency to purchase operational infrastructure in a way that aligns with North Korea’s juche state ideology of self-reliance, therefore reducing the fiscal burden on the central government.”
In addition, APT43 – known as Kimuski – likely uses hash rental and cloud mining services to launder the stolen cryptocurrency “clean”. To financially support the infrastructure, PayPal, American Express cards and “Bitcoin probably derived from previous operations” – the payment methods the group used.
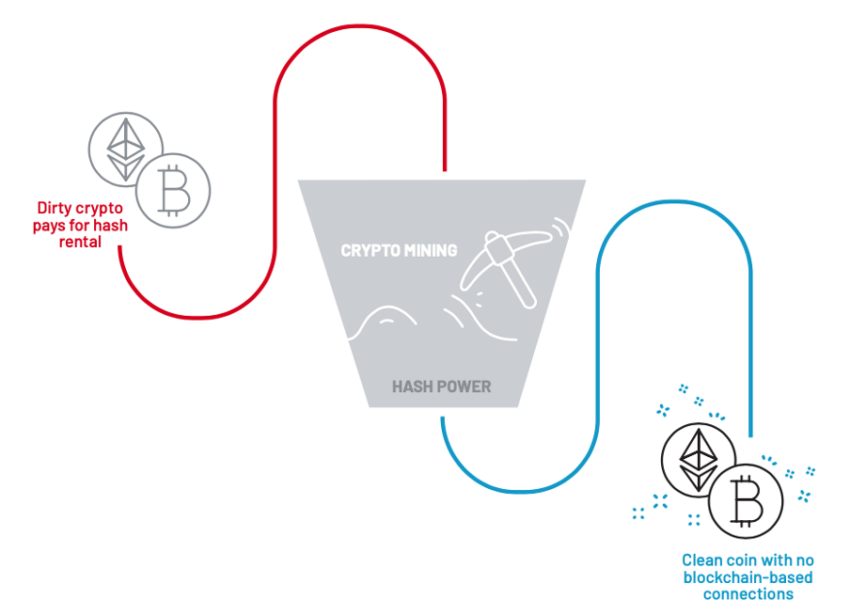
Understand the process
Hash rent and cloud mining are legitimate services many use for cryptocurrency mining. However, hackers can also use these services to launder stolen cryptocurrency.
In this scenario, the hacker first steals a large amount of cryptocurrency from a victim. They then use the stolen cryptocurrency to purchase hash power from a hash rental or cloud mining service. With the extra hash power, hackers can mine more cryptocurrency than they could.
Once mining is complete, the hacker can sell the newly mined cryptocurrency in exchange for pure cryptocurrency unrelated to the original theft. By using hash rental and cloud mining services in this way, the hacker can make it difficult for the police to trace the stolen funds.
It is important to note that while hash rental and cloud mining services can are used for illegal activities, they are not illegal. However, individuals and businesses must secure their cryptocurrency wallets and ensure that they are not vulnerable to hacking attempts. Additionally, exchanges and other cryptocurrency businesses should have measures in place to detect and prevent money laundering activities.
Overall, governments around the world have become more aware of the potential for illegal activities funded by cryptocurrency. Regulators are taking steps to regulate the industry. As a result, it is becoming increasingly difficult for spies to use cryptocurrency to finance their operations without detection.
Disclaimer
In accordance with Trust Project guidelines, this feature article presents the opinions and perspectives of industry experts or individuals. BeInCrypto is dedicated to transparent reporting, but the views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of BeInCrypto or its employees. Readers should verify information independently and consult with a professional before making decisions based on this content.


