Make NFT trading cheaper with aggregation, security and tokenization
If you want to buy or sell an NFT, you have almost a dozen mainstream options today. To an outsider, they all look the same, with their homepage walls of square cartoon characters.
However, there is an evolution underway from standard buy-and-sell marketplaces – OpenSea, X2Y2, LooksRare – to models that try to make NFT trading cheaper through innovative solutions. In this article, we will explain the three most important new ones: aggregation, security and tokenization.
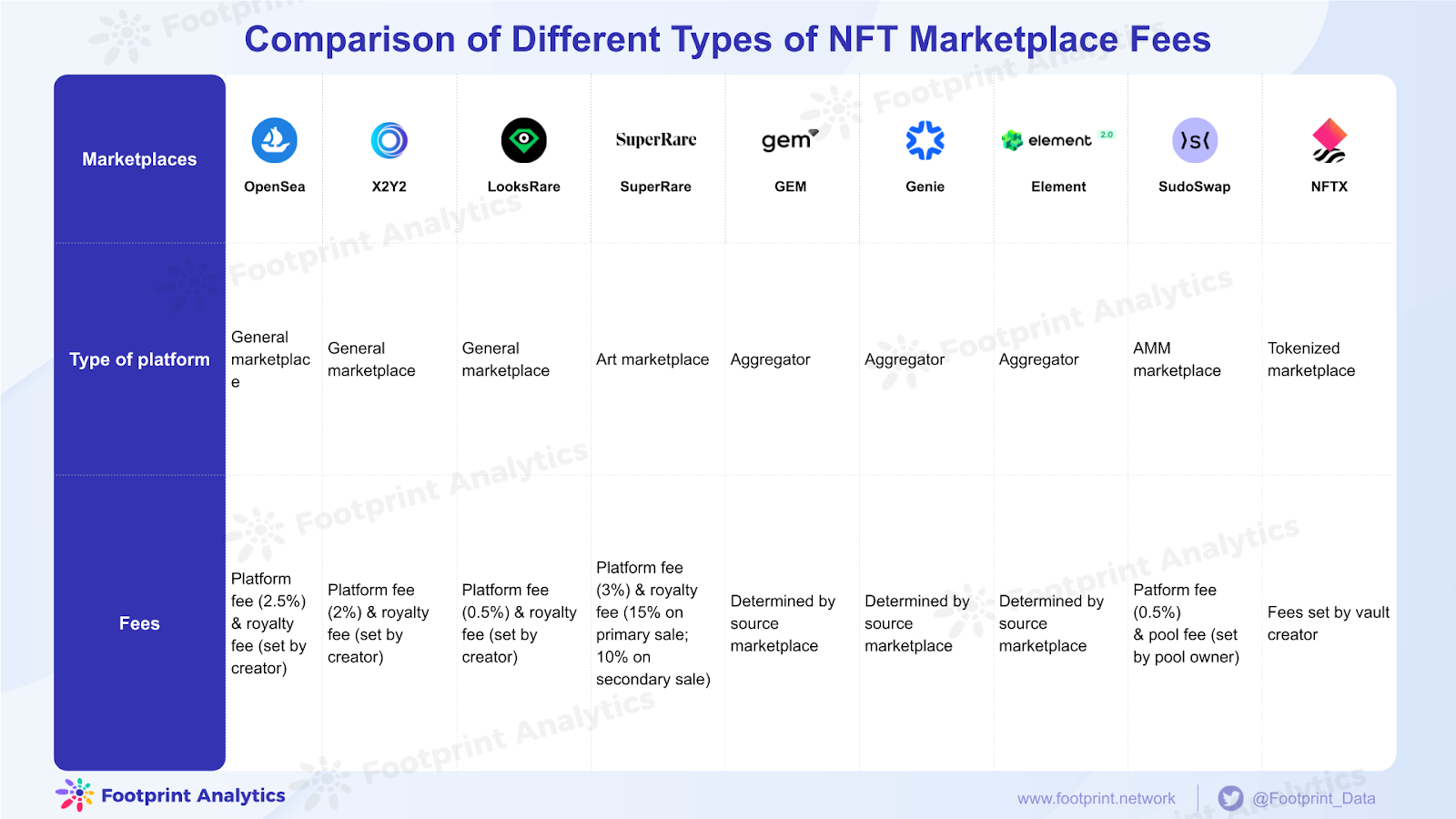
What are general and art NFT marketplaces?
A general marketplace is a platform that sells a wide range of NFTs. An art marketplace hosts a select selection of researched artists and collections. Unlike a general marketplace where anything goes, art marketplaces use curation to give their platforms a desired aesthetic.
Most NFT trading markets allow Trader A to sell his assets at a set price. When Trader B is willing to pay this price, the trade takes place. This behavior is generally known in the market as the “buy now” approach. OpenSea, LooksRare, X2Y2 and SuperRare trade on this fixed price basis.
Another method is to bid with other buyers, just like a traditional auction market, and the highest bidder gets NFT assets. Open sea is an example of such a marketplace.
In both cases, buyers must pay gas fees for transactions, and lack of liquidity makes NFT trading inefficient.
What are NFT Aggregators?
A persistent problem in the NFT market is spending too much time and gas buying more NFTs.
Not to be outdone by the rapidly growing trend of the NFT marketplace, OpenSea, the premier trading marketplace, announced on October 5 that it officially supports bulk listing and buying functionality, allowing users to now bulk list and buy up to 30 items in a single transaction on OpenSea .
According to the data, while OpenSea has integrated bulk buying of a single collection, making life easier for less active traders, serious NFT traders will still find it difficult (and expensive) to trade all these different marketplaces when trading.
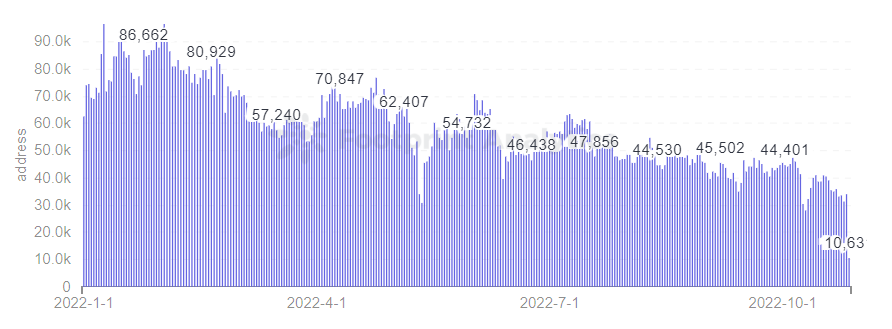
Footprint Analytics – OpenSea daily active users
GEM, Genie and Element marketplaces are new platforms that bring together several marketplaces. Instead of comparing prices on different sites, aggregators have all the data in one place and can also buy in one place. This allows NFT enthusiasts to save time and money (in gas fees) when purchasing multiple items.
Furthermore, GEM (but not Genie yet) accepts all ERC-20 tokens as payment. This allows users to make one payment with a range of matching tokens of their choice.
What is an AMM NFT Marketplace?
Sudoswap is a decentralized on-chain NFT exchange that uses the AMM model.
An AMM (automatic market maker) in DeFi refers to a dispersion asset trading pool that allows users to seamlessly trade cryptocurrencies through their liquidity.
The operating mode of AMM is different from the traditional order book transaction mode. Both parties in the transaction to AMM interact with the liquidity pool in the chain. Liquidity pools allow users to seamlessly switch between tokens on the chain in a fully decentralized and non-custodial manner. Liquidity providers (LPs), on the other hand, earn passive income through transaction fees, which are based on a percentage of their contribution to the asset pool.
NFTs tend to be volatile because they lack liquidity, and Sudoswap brings some of the features from DeFi to the NFT market.
- Users can buy or sell from different pools in the NFT collection
- Pools can buy or sell to different users
- Users can create NFT liquidity pools with ETH within the same pool
What is NFTX?
NFTX where users can post collateral and tokenize their NFTs, which the platform hopes will solve the problem of liquidity in the NFT market. An NFT holder can transfer their digital assets to a vault and mint fungible tokens (vTokens) that represent the NFT’s value. For example, a CryptoPunk NFT creates a corresponding fungible CryptoPunk vToken.
Users selling NFTs on NFTX are equivalent to minting an ERC-20 token and paying a 10% coin fee, which they can exchange for ETH on SushiSwap. The tokens are fungible, that is there is sufficient liquidity in the NFTX pool. To remove NFT from the vault, a user must deposit a fungible vToken.
Critically, a user can easily exchange their NFTX token for another on a DEX, essentially bypassing the longer and more expensive process of exchanging one NFT for another on a marketplace.
Summary
NFTs are blockchain tokens, but do not function as such – they are illiquid and inefficient to trade. Several new models of NFT marketplaces have emerged to address this issue and make trading NFTs a smoother process.
This piece is contributed by Footprint Analytics society.
Footprint Community is a place where data and crypto enthusiasts around the world help each other to understand and gain insights about Web3, the metaverse, DeFi, GameFi or any other area of the new world of blockchain. Here you will find active, diverse voices that support each other and drive society forward.
October 2022, Vincy
Data Source: Footprint Analytics – NFT Marketplaces
Footprint website:
Disagreement:
Disclaimer: Views and opinions expressed by the author should not be considered financial advice. We do not provide advice on financial products.


