Writing in the journal SustainabilityLewis A. Njualem of California State University in San Bernadino, California, has explored the application of blockchain technology to improve supply chain sustainability.

Study: Leveraging Blockchain Technology in Supply Chain Sustainability: A Provenance Perspective. Image credit: elenabsl/Shutterstock.com
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is an emerging, disruptive technology. While considerable focus has been placed on the use of cryptocurrencies in the media in recent years, blockchain technology has several potential benefits for many industries.
Blockchain technology uses a distributed, decentralized database or ledger to store information digitally. The main advantage of blockchain technology is to guarantee the safety and credibility of data, generating trust without the need for a third party. Data is stored in chronological blocks, which are chains of groups of data that, when full, are linked to other blocks. This forms a chain of data, which is known as the blockchain.
With the blockchain, digital information can be recorded and distributed, but cannot be edited. This creates an immutable ledger, which is permanently available as it cannot be changed or deleted. For this reason, another name for blockchains is distributed ledger technology.
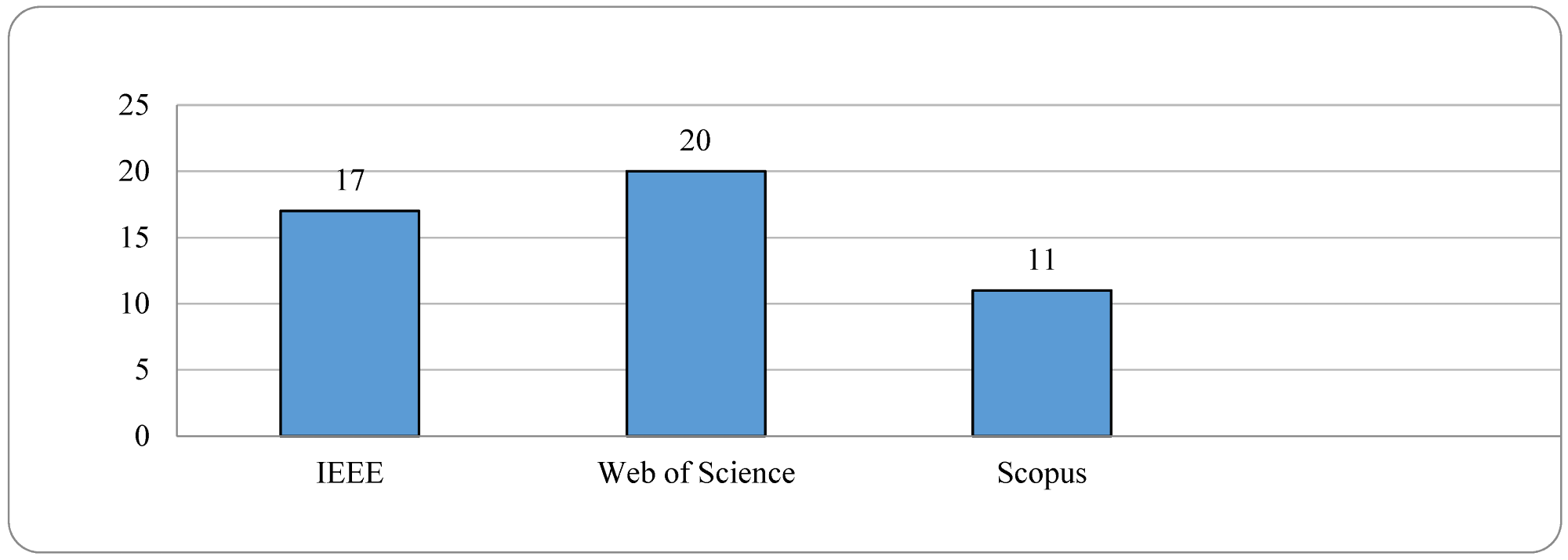
Initial search results for articles by source. Image credit: Njualem, LA et al., Sustainability
Supply chains: requirements and challenges
Supply chains are an integral part of every industry, from manufacturing to the energy sector, mining, transport and biomedical industries. Commercial goods come from a variety of sources and can end up in multiple locations where the end user is located. Supply chains are complex and time-sensitive, especially in today’s hyper-globalized world.
Flexible production and the expansive nature of the supply chain create more challenges for delivering commercial goods to customers. For example, one of the main challenges facing supply chains is changing consumer preferences, especially when it comes to sustainability and provenance. Consumers increasingly demand knowledge about where their products come from and their carbon footprint.
Track and trace are important elements of supply chain distribution that help meet these consumer demands and improve provenance. However, this can be complicated by a number of factors. Different BOMs are used for several components and raw materials, which is a widespread practice in, for example, the automotive industry.
In the case of the automotive industry, several alternative components are available for customization purposes, which can further complicate provenance challenges, as customers do not always know exactly where these components come from. Improving provenance information helps consumers and downstream companies about the sustainability of the products they buy.
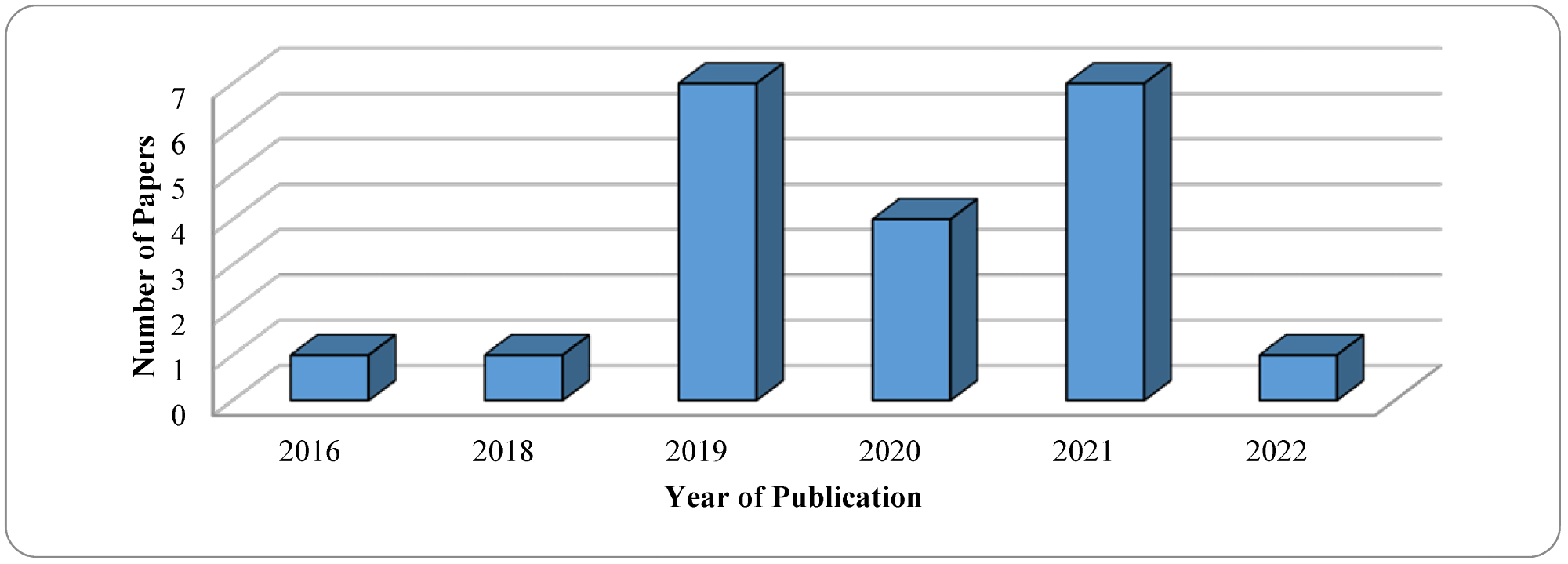
Result for the publication year of the article. Image credit: Njualem, LA et al., Sustainability
The research
The paper has evaluated the use of blockchain technologies to improve provenance and sustainability in manufacturing supply chains. So far, there is a lack of research on the use of the blockchain outside of the financial and cryptocurrency sectors. The study aims to help fill this important knowledge gap, recognizing the potential for blockchains to improve multiple industries.
Studies on the application of blockchain technologies outside the financial sector have also mainly concentrated on specific supply chains. This is usually from an industry perspective and has not considered the effects on supply networks. The new article aims to address provenance issues throughout the value chain in relation to raw materials, components and finished products.
Three main questions are explored within the research. First, the paper examines how much research has been conducted on the use of blockchain technologies to improve supply chain sustainability. Second, the study explores the known benefits of supply chain visibility technology. Thirdly, it explores current challenges related to ancestry.
Appropriate methods have been used in the research to establish a platform for analyzing current research in this emerging field. A content analysis method has been applied to the relevant literature. Text analysis is used to enable data collection, analysis and key concept synthesis.
Through thorough analysis and interpretation of current research, the study aims to motivate future studies in the application of blockchain technology to questions about the origin and sustainability of the supply chain.
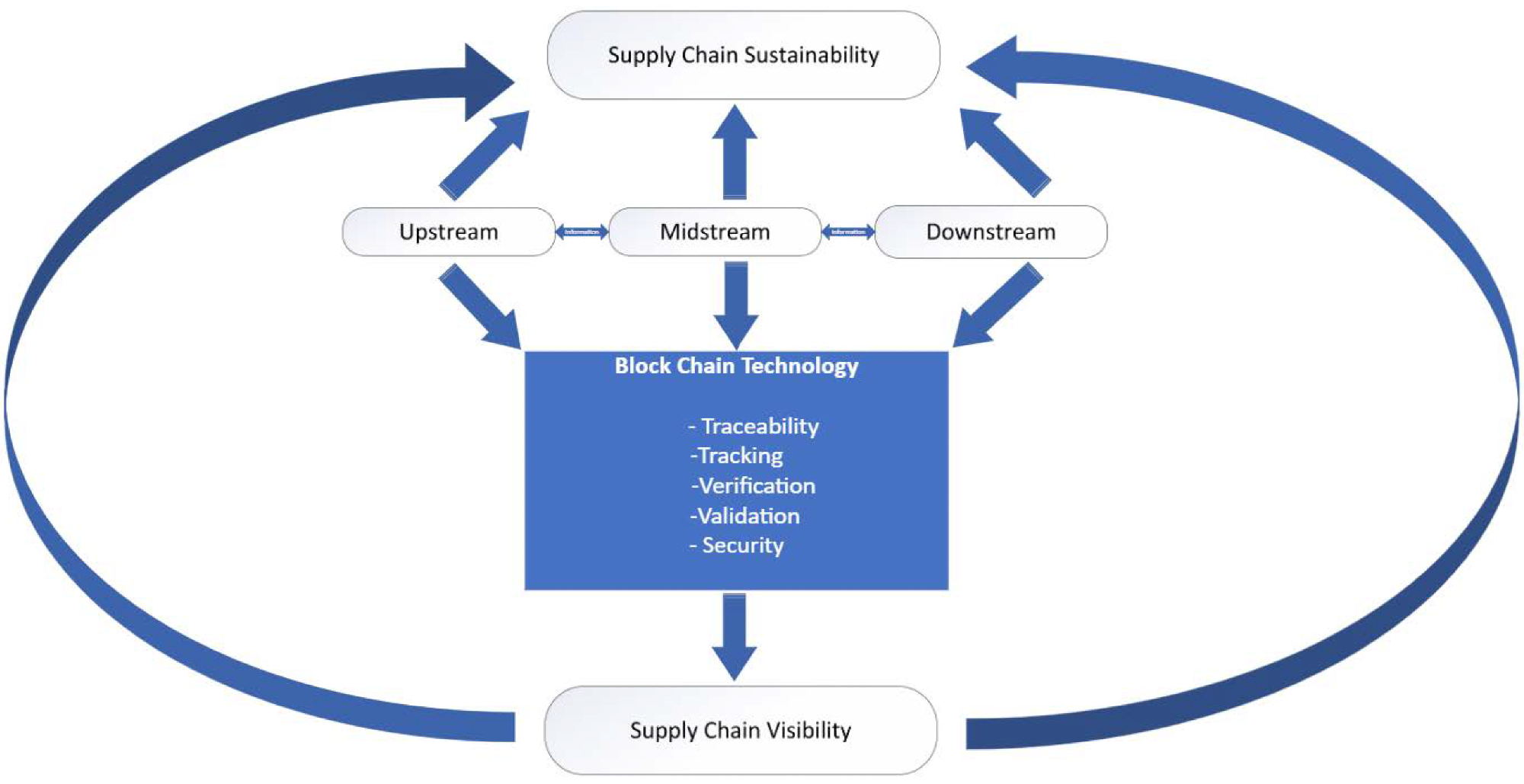
A conceptual model for blockchain-enabled sustainable supply chain visibility. Image credit: Njualem, LA et al., Sustainability
Study findings and conclusions
The complexities of the modern globalized supply chain affecting sustainability and provenance have been the main drivers to explore innovative solutions such as blockchain technology, leading to a growing paradigm shift. Several studies in recent years have confirmed the increased research interest in applying these technologies in the sector.
Blockchain technologies provide enhanced capabilities to meet these requirements compared to other disruptive innovations, such as IOT and RFID, due to decentralization and immutability. This capability allows blockchains to improve security, trust, transparency and accountability. Indeed, some companies have already made inroads into the use of blockchains, such as Walmart and IBM.
However, there are some challenges with this emerging field of research. First, as it is in its infancy, studies are limited. Moreover, technical issues of control, regulation, scalability and knowledge exist, affecting factors such as the visibility of sustainable supply chains.
There are other bottlenecks with provenance, such as crime, different government regulations and culture, which need to be assessed by researchers. The novelty of the technology may cause several challenges, but the field is very promising. The article’s analysis and observations help lay the foundation for future study and help identify new paths in research.
Further reading
Njualem, LA (2022) Leveraging blockchain technology in supply chain sustainability: a provenance perspective Sustainability, 14(17), 10533 [online] mdpi.com. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/14/17/10533


