Researchers from the University of Cambridge, Tesla and the University of Strathclyde have investigated the use of blockchain technology in smart grids. Their research has appeared in the journal Energies.

Study: Impact of blockchain technology on Smart. Grid. Image Credit: MiniStocker/Shutterstock.com
The changing face of energy generation in the 21st centurySt Century
Rapid global population increase since the early 20th centuryth Century has facilitated the need for reliable and efficient energy production to provide a good quality of life for individuals. Progress in modern society and industry is intrinsically linked to the use of fossil fuels, which are becoming increasingly unsustainable due to climate change and resource depletion.
The transition to a low-carbon economy is a central area of discussion in the 21st centurySt century, and the recent energy crises due to geopolitical and economic instability have focused the attention of researchers, industry and government bodies on alternative solutions to meet the increasing demands of the modern world.
In the EU, aggressive targets have been introduced that aim to produce 100% of the area’s energy production capacity from renewable sources, with a preliminary target of renewable energy covering 32% of energy needs by 2030. However, there are several key technical and infrastructural areas. challenges that must be overcome to transition to a net-zero carbon economy while ensuring access to reliable energy.
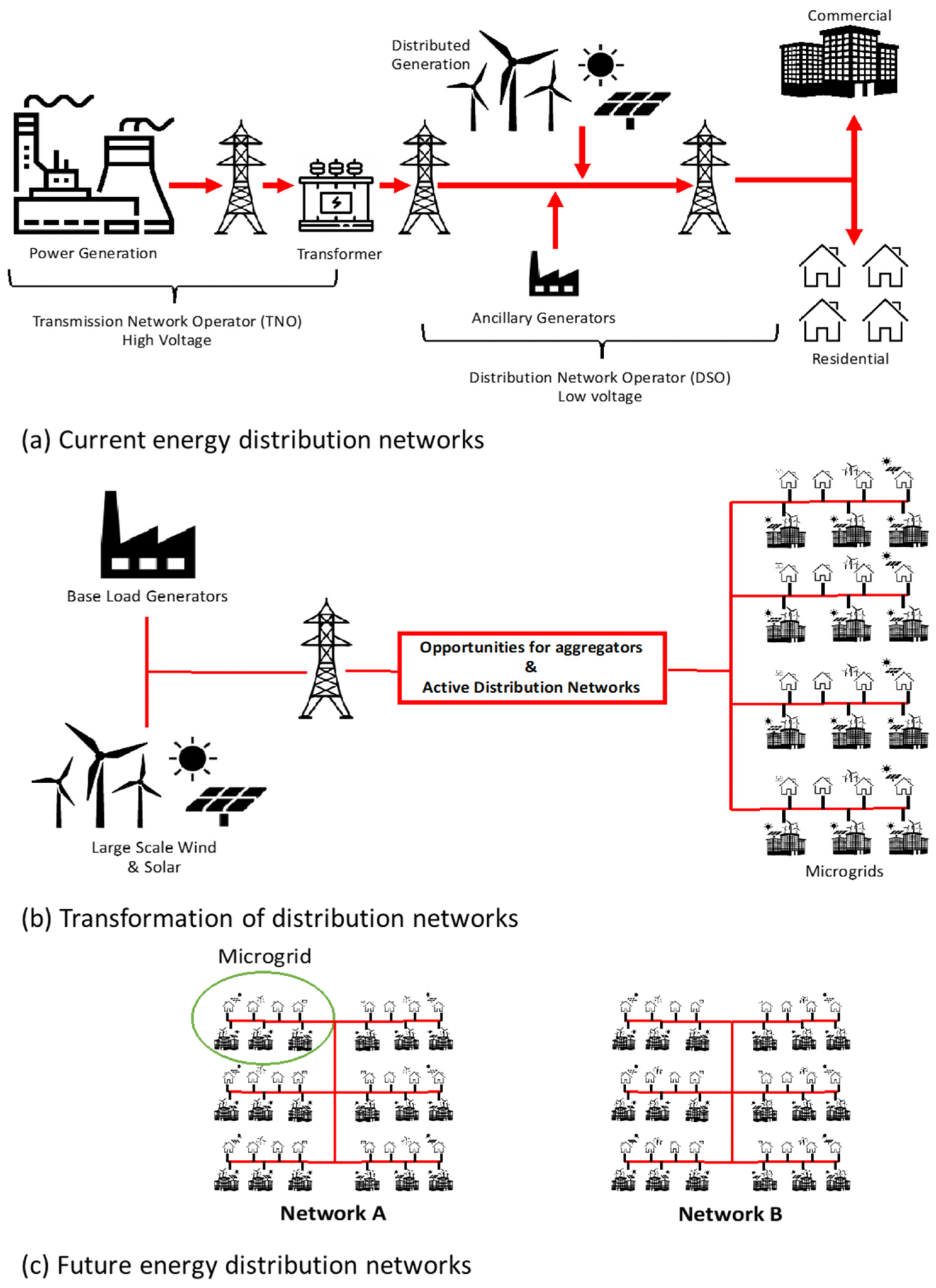
Transformation of the distribution network. Image credit: Khan, H & Masood, T, Energies
Decentralized grids: A future solution to the energy and sustainability crisis?
Currently, national energy grids are mainly centralized, with a small number of producers and distributors supplying electricity to commercial and domestic consumers. Additional systems provide emergency backups such as power outages to balance the grid as and when needed.
However, the ongoing geopolitical situation and historical crises, such as the oil crisis of the 1970s, have demonstrated the fragility of centralized power supply and the catastrophic consequences on society and the global economy. The critical nature of reliable and affordable energy supply has led researchers, companies and governments to explore decentralized energy grids.
In a decentralized grid, there are multiple buyers and sellers, with many microgrids supplying consumers and prosumers. However, to move to a fully decentralized, sustainable and green grid with many smart elements, there are many regulatory and technical challenges that need to be overcome at multiple levels by players in the energy industry and related sectors.
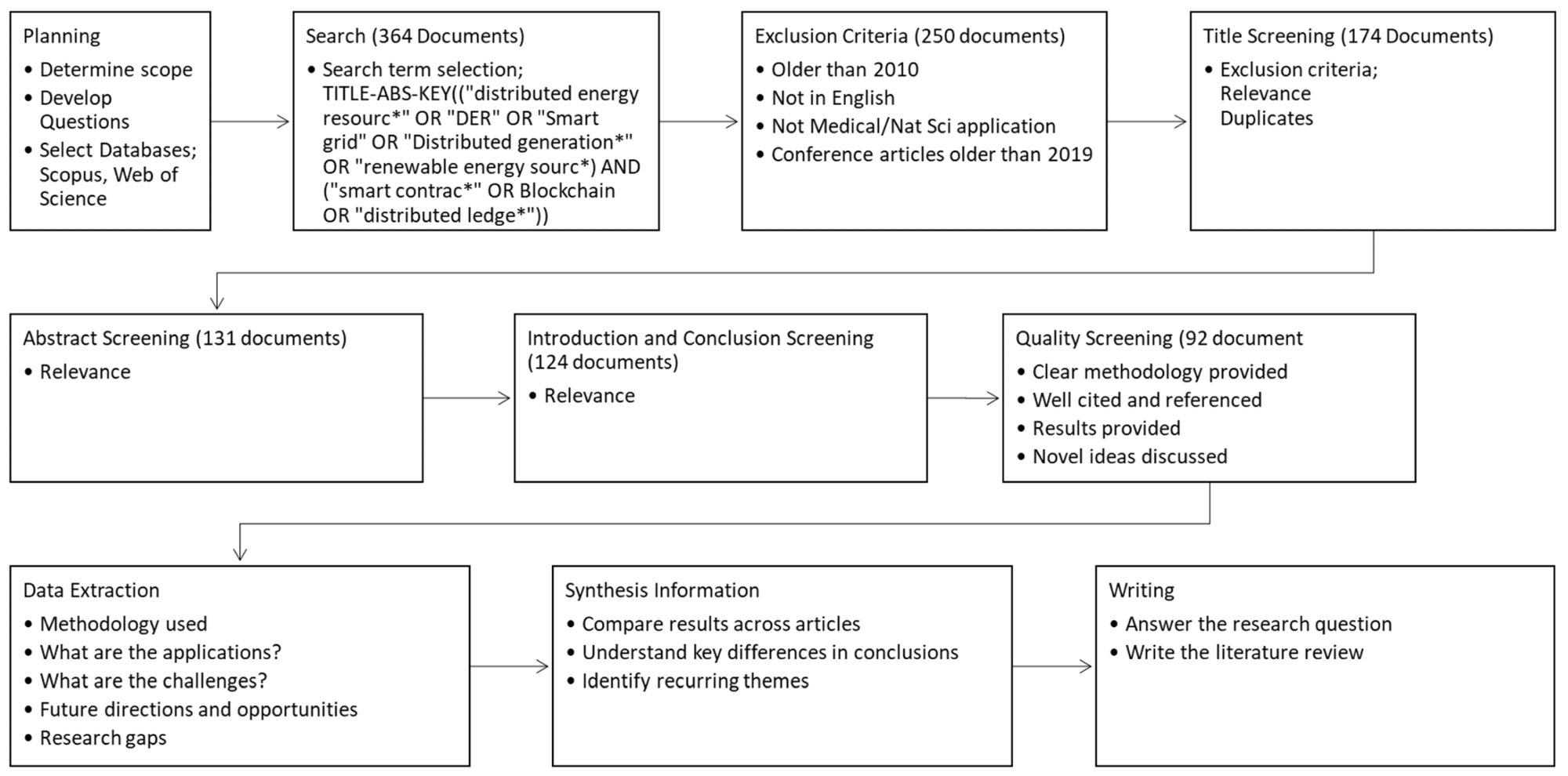
The method followed to conduct this systematic literature review. Image credit: Khan, H & Masood, T, Energies
The newspaper
The new research in Energies have explored the use of blockchain technology in proposed smart grids. Blockchain is a disruptive technology that is playing a growing role in many industries and sectors, particularly the global financial system, where it powers cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Blockchain technologies are based on the concept of decentralization and use a distributed database, also referred to as a ‘ledger’, to digitally store information and provide provenance information for transactions. One of the advantages of blockchain is the fidelity and security of the data in the ledger without the need for a third party to generate trust. Data is stored in a chain of “blocks”, hence the name, which are linked together chronologically.
The article has provided a thorough analysis of potential and current perspectives in the application of blockchain technologies and aims to identify key research areas within these new technology fields. Research gaps and future opportunities have been identified and discussed in depth by the authors.
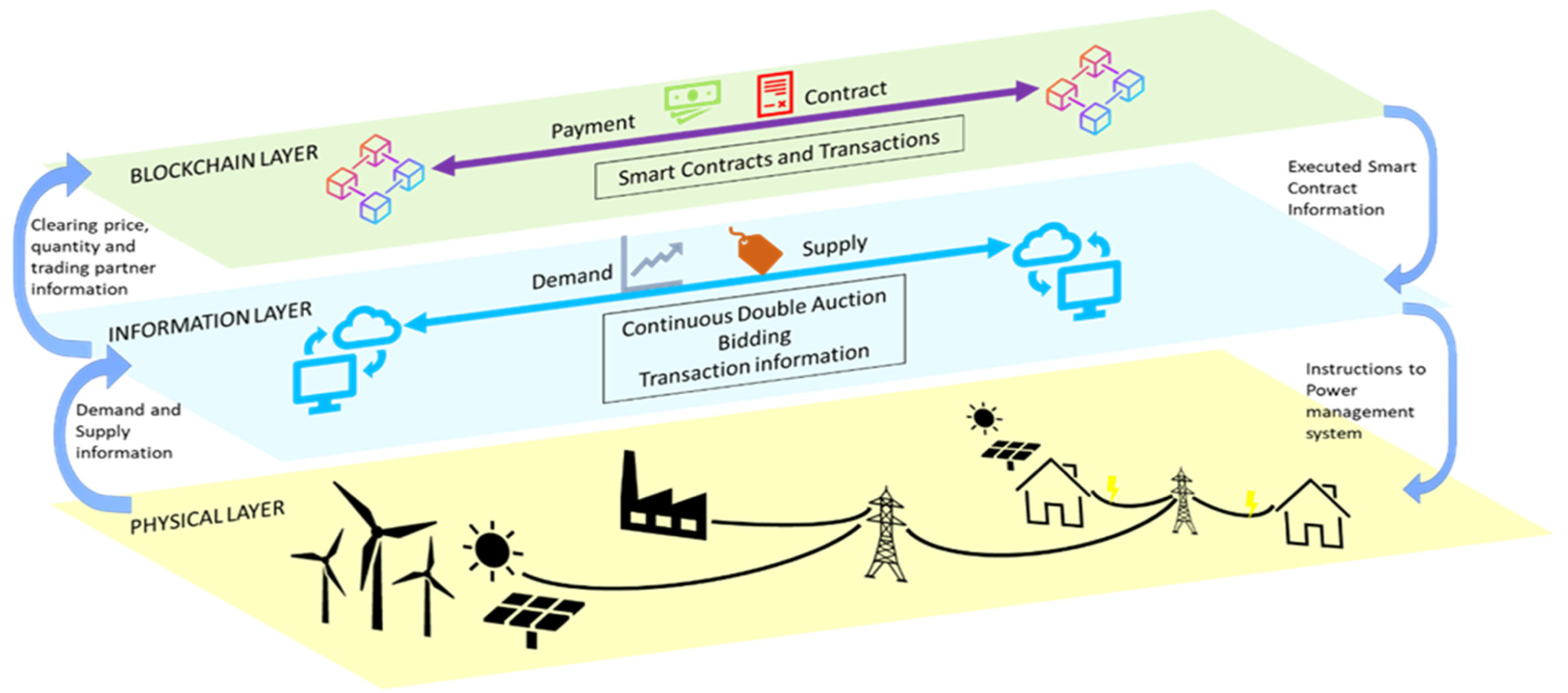
A type of blockchain-based decentralized energy distribution system. It can be seen how different areas of research discussed in this article fit together to form a blockchain-based energy distribution system. Image credit: Khan, H & Masood, T, Energies
Study findings and conclusions
A systematic literature review was carried out to identify opportunities and gain a comprehensive understanding of the research question. Four review questions were developed by the authors to guide the review: What are the main areas where blockchain is being used? What research methodologies have been used? What challenges are linked to the use of blockchain for smart grids? Finally, what are the research gaps?
Currently, the use of blockchain technologies in the smart grid energy industry is limited, with some notable projects such as the Brooklyn Microgrid Project demonstrating their potential. There is still a long way to go until the technology is fully adopted, and several challenges must be overcome.
Ethereum has emerged as the most popular blockchain technology for smart web applications, but the authors have noted that this is due to convenience rather than need. Several studies in the current literature have highlighted that blockchain technologies can potentially meet the needs of smart and decentralized energy grids, increasing efficiency and lowering costs.
The review has classified research into four main categories: Electric vehicles, P2P commerce, privacy and security, and demand response. Six important research gaps were identified. A main gap highlighted is blockchain technology scalability issues. Resource and time constraints affect the use of blockchain technologies, especially if large amounts of continuous transactions are required.
A future research opportunity highlighted in the review is the development of more accessible systems based on blockchain technologies. A main concern is privacy and security with smart contract settlements in decentralized energy transaction systems due to the creditor’s access to personal data. More accessible systems can help address this concern and other issues.
More tools will need to be developed to overcome the current challenges of using blockchain technologies in smart energy grids, and significant research in this area will be necessary to help realize its full potential. The new review in Energies has provided a timely and important overview of the current state-of-the-art in this emerging technological field.
Further reading
Khan, H & Masood, T (2022) Impact of Blockchain Technology on Smart. Grid Energies, 15(19), p. 7189 [online] mdpi.com. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/15/19/7189


