Block structures in the block chain | by Kacper Hernacki | July 2022
Blockchain is a chain of data, which is represented in blocks. It is the basic part of web3 implementations and decentralized solutions. Each block must include data stored in the blockchain.
Have you ever wondered how it does it and what data it consists of?
Are you curious about how blocks are connected in links?
in that case it is the resource for you …
Agenda:
- block structure,
- Heading,
- Previous hash details,
- Timestamp,
- Nonce,
- Merkle three,
- Body,
- Block types,
- When the block is orphaned.
Each block is made of header and body. Both store data, but slightly different and for other purposes.
The block structure is essentially the same in different ecosystems, there may be some changes in the data format and information about transactions, because blockchain can also be used in other industries.
Heading
The heading of a block represents:
- former hashish,
- Timestamp,
- Nonce,
- Merkle root
The hash for the previous block is calculated by transferring the heading of the last block to the hash function. Hash algorithm prevents blockchain from hacking, because even a small change in a header and hash result is completely different. Moreover, it is impossible to calculate the header from the result.

The timestamp is used as proof that the block was extracted in a specific moment and is the decisive element in the argument in the hash function. One second of change and calculated hashish is different.
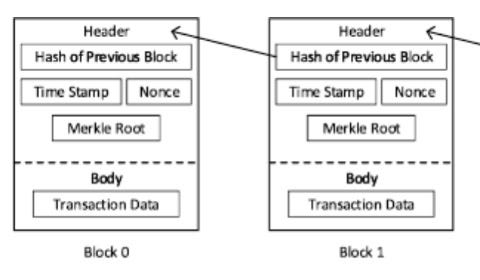
Nonce is the number that is only used once, which miners in the blockchain solve for. Once solved, a new block can be added. This number is 4 bits long, and it takes about 10 minutes to search for it in the bitcoin ecosystem.

Merkle-tree is a binary tree, in which each leaf node is marked with a hash of one transaction, included in the block body. The Merkle tree is used to reduce the effort to verify the transactions in the block.
Body

The block body is the main part of stored data. It is the place where transaction data is stored and ready to read from blockchain explorers.
Types of blocks
- genesis block,
- – Valid blocks,
- – Orphaned blocks,
The Genesis block is the first block in the blockchain ecosystem, the whole system is built on them.
Valid blocks are all mined and approved blocks.
Orphan block is a mined block, but not attached to a block chain.
Block is orphaned in a situation when two miners add a new block at the same time, but the system must decide which one should be part of a block chain.
Also, when there is a hacker attack, the situation may be similar. “Injected” block is not correct, so it is not attached.
Join my web3 challenge and follow new content:

- Twitter: https://twitter.com/kacperhernacki
- Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/kacper.hernacki/
- LinkedIn: https://pl.linkedin.com/in/kacper-hernacki-965161203
- Github:


