Bitcoin does not react to monetary and macroeconomic news
Bitcoin, the cryptocurrency’s flagship coin, has been a gray area, i.en relation to both monetary and macroeconomic factors. Various regulators, such as the New York Federal Reserve, are diving deep into this relationship and the ramifications the asset class may or may not have.
Various factors, including monetary and macroeconomic news, affect Bitcoin’s price. While it is true that Bitcoin is a relatively new and distinct asset class, it is still subject to many of the same market forces as traditional asset classes.
For example, when there is news that suggests inflation is rising or the value of the US dollar is falling, this can cause investors to turn to Bitcoin as a potential hedge against inflation and a store of value. However, some questions have been asked on this topic.

Conversely, positive economic news, such as solid job growth or a rising stock market, can cause investors to move away from Bitcoin and towards more traditional assets. Furthermore, Bitcoin has been known to experience significant price fluctuations in response to regulatory announcements or changes in government policy. For example, when China banned cryptocurrency trading in 2017, the price of Bitcoin dropped significantly.
Understand the relationship
While Bitcoin may not be directly correlated with all traditional asset classes, it is still subject to many of the same market forces, including financial and macroeconomic news. To shed more light on the relationship, the Federal Reserve Bank of New York published a report that analyzed the impact of macroeconomic factors on the price of Bitcoin.
The FED report titled “The Bitcoin–Macro Disconnect” discussed the difference between the behavior of Bitcoin and the macroeconomic factors that typically affect traditional asset classes. The report notes that Bitcoin has shown little correlation with measures of economic activity such as inflation, interest rates and economic growth. In addition, Bitcoin has shown higher volatility than other assets, with significant price swings occurring in short periods of time.
The cumulative crypto market capitalization reached $2.50 trillion in 2021, and Bitcoin’s market capitalization reached $1 trillion. Fast forward, BTC saw a significant correction last year. Nevertheless, various macro factors influenced BTC’s past price action. To assess this, the authors have analyzed specific macro factors that affect the price. In other words, they considered BTC’s price action when it appeared to be directly related to a macro factor, not a crypto-specific factor like the collapse of FTX.
Crypto and market manipulation
Therefore, the report divided these macro factors into three categories: news about the real economy and unemployment statistics. News about inflation, such as the consumer price index or CPI, and information about monetary policy, such as interest rate changes or the Fed’s intention to change interest rates in the future.
The authors specified that they looked at how BTC’s price responded to these macro factors between 2017 and 2022. This is because BTC reached a “more mature stage” starting in 2017. This appears to refer to the launch of Bitcoin Futures on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange used of institutions at the end of 2017.
Many argued that this launch of Bitcoin Futures on the CME was when institutions began to manipulate the crypto market. Market manipulation has since extended to other cryptos, namely Ethereum (ETH), which is now also on the CME.
Macro factors defined
The report then unpacks how the authors modeled BTC as a speculative asset with no intrinsic value. It states that the BTC price is determined by interest rates which in turn are determined by macro factors. For context, debt becomes cheaper and easier to borrow when interest rates are low. This increases the total money supply, which causes prices to rise.
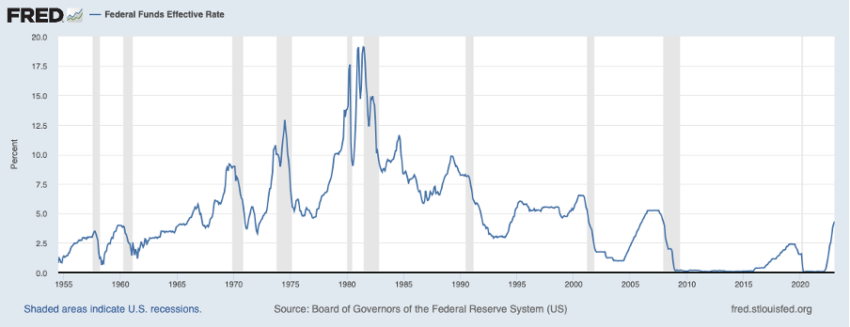
Interest rates have remained low since 2008, which is reflected in several asset classes rising. When interest rates are high, debt becomes more expensive and more difficult to borrow. This reduces the total money supply, which causes prices to fall. This has been the case since the Fed announced that it aimed to raise interest rates in November 2021. The catch is that the Fed began raising interest rates in the spring of 2022.
Nevertheless, markets reacted because investors would want to capitalize on potential effects, always pricing what will happen in the future. Keep in mind that this guidance going forward is one of the three macro factors the authors included in the report. This leaves unemployment and inflation. These are relevant for the interest rate because most central banks have been explicitly instructed to ensure that both unemployment and inflation remain low.
Conclusion from the report on Bitcoin
As far as the Fed is concerned, the unemployment and inflation targets are somewhere around four percent and two percent, respectively. Central banks also follow the guidance and achieve this dual mandate by changing interest rates. Higher interest rates lead to lower inflation, but higher unemployment, and vice versa. This is why investors have been eagerly awaiting every inflation statistic – lower inflation means the Fed will cut interest rates.
(Increased money creation may trigger some rise for the financial market, especially risky assets like BTC.)
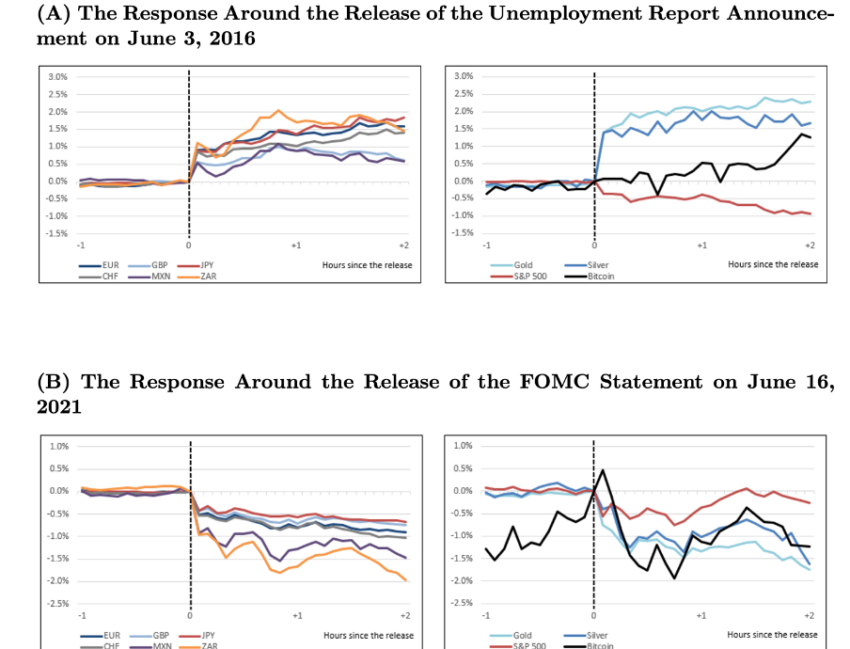
Carlo Rosa spoke with one of the authors and shared an important screenshot with BeInCrypto. It said:

Bitcoin is orthogonal to monetary and macroeconomic news. “This disconnect is puzzling as unexpected changes in discount rates should in principle affect the price of Bitcoin even when interpreting Bitcoin as a purely speculative asset,” the author added.
Bitcoin, compared to other asset classes
The largest cryptocurrency market cap grew from $1 billion in 2013 to over $1 trillion in 2020. The average annual return since 2012 was almost 3 times per year. In contrast, the average annual return for the S&P 500 was only 11% per year. During the same period, gold and silver remained flat.
The Fed accepts the need for more study to understand the mismatch between Bitcoin and macroeconomic issues. According to the research, “the finding that Bitcoin does not respond to monetary news is intriguing as it raises some concerns about the importance of discount rates in the pricing of Bitcoin.”
On the other hand, after the report, social media platforms like Twitter saw more reactions. Here is one of the reactions:
Overall, according to the Fed report, Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies are viewed as speculative assets that are still maturing compared to other asset classes. Only time will tell if BTC will be a challenger to the US dollar.
Disclaimer
All information on our website is published in good faith and for general information purposes only. Any action the reader takes on the information contained on our website is strictly at their own risk.


