Asset seizure was possible in original Bitcoin
On July 28, 2010, users discovered that they could “steal” someone else’s Bitcoin by simply putting OP_TRUE OP_RETURN in front of a locked script. Since the OP_RETURN opcode stops script execution (like a return function in any programming language), it will return the previous value on the stack, OP_TRUE, which returns a true state that allows the use of someone’s coins, regardless of the spending conditions.
This “bug” was quickly patched by Satoshi Nakamoto, changing the functionality of OP_RETURN to immediately return false instead. However, with the understanding that Bitcoin does not operate outside the law and miners would not realistically process transactions with this script, even if it were technically possible, we can now question whether this was just a technical oversight.
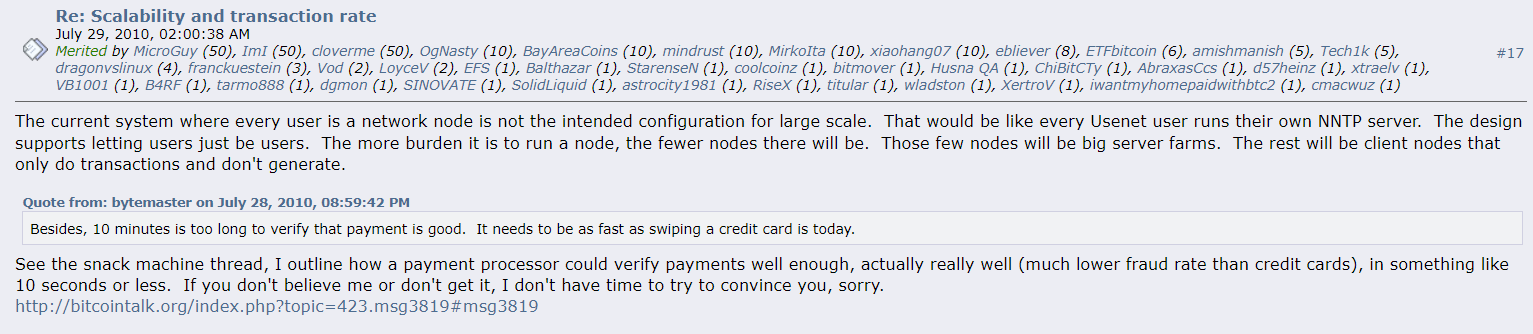
Satoshi infamously stated that he believed “few nodes will be large server farms.” When we think through this, this implies large corporations that would not allow crime to happen with impunity on their watch. Furthermore, these large corporate nodes would comply if instructed to freeze orders or seize assets from the authorities. This communication capability was implemented in Bitcoin early on also via the notification system. BTC Core developers removed this functionality in 2016.
Today, many in the digital currency space believe that seizing and freezing assets is technically impossible, since the system is “decentralized” and it cannot be done due to “simple math.” The reality is that the creator had implemented puzzle pieces for this to be possible from the early stages of the network, but due to its immaturity, the subsequent removal of these features has allowed newcomers to control the narrative of Why they were removed. For example, regardless of Nakamoto’s intent, BTC Core provided its own subjective, interpretive reasons for why the notification system should removed:


The original features did not scale due to the fact that nodes could be run on home computers with little or no capital investment. Unlike large corporations that generate millions in revenue and must be registered legal entities, these home users cannot be trusted to follow legal instructions or not steal other people’s assets.
Craig Wright explains this in March 2020:
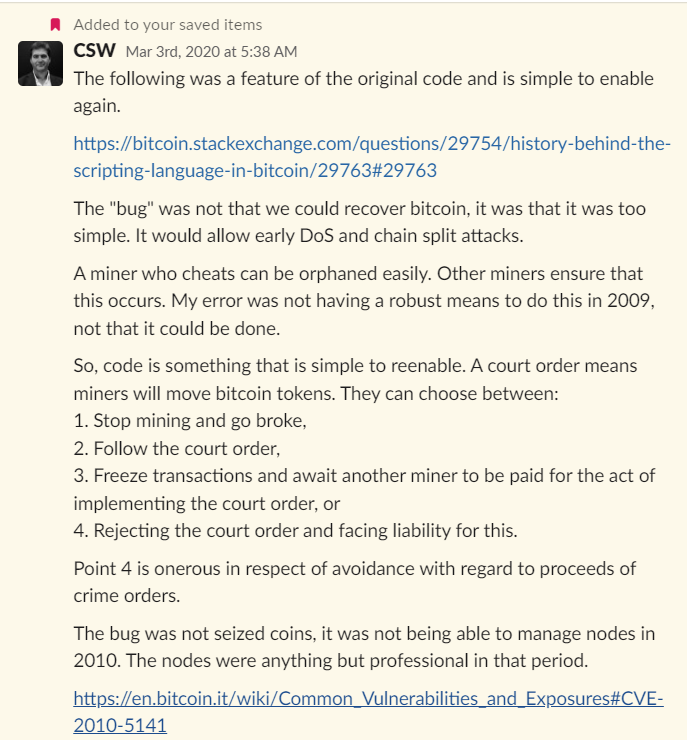
Even if the OP_TRUE OP_RETURN bug was technically possible on Bitcoin today, nodes would likely reject these scripts as they would essentially be guilty of facilitating crime. Therefore, a simple re-implementation of this “bug” from the original version of Bitcoin will implement the technology that is possible for miners to be able to freeze and return assets despite the fact that the “experts” claim it is impossible.
If the implemented solution does not make OP_TRUE OP_RETURN scripts possible, then another agreement with nodes is via a notarized contract. Nodes can now receive instructions from court orders to freeze assets or reallocate coins. This implementation by the Bitcoin Association echoes Wright’s sentiments in February 2022, doubling down on the concept that network consensus should be achieved outside of the technicalities of the blockchain:

This concept is a reminder that we live in the real world. Just because something is technically possible to achieve does not mean it is morally right or legal. Bitcoin cannot scale to be money for the world if loss of possession results in loss of ownership, Unlike any other asset in the world. It’s also worth noting that the original Bitcoin white paper says that nodes protect “ownership” and not “assets”.
After all, Joseph Vaughn-Perling stated that this was crucial to Bitcoin’s mass adoption in May 2016:

See: Digital Asset Recovery on Bitcoin Explained
width=”562″ height=”315″ frameborder=”0″ allowfullscreen=”allowfullscreen”>
New to Bitcoin? Check out CoinGeeks Bitcoin for beginners section, the ultimate resource guide for learning more about Bitcoin – as originally envisioned by Satoshi Nakamoto – and blockchain.


