All investment/financial opinions expressed by NFTevening.com are not recommendations.
This article is educational material.
As always, do your own research before making any kind of investment.
all about cryptop referances
Dynamic NFTs are the key to unlocking the full potential of Web3. Unlike traditional tokens, dynamic NFTs or “dNFTs” change over time based on external conditions. This capability has created many compelling new use cases for digital assets and is changing the way we think about NFT technology.
Dynamic NFTs are “living” tokens. They respond to external triggers such as price fluctuations, user behavior, time, weather, etc. These moving data points can be used to update the metadata of dNFTs, thus allowing them to transform over time to evolve with the world around them.
For example, imagine an NFT representing a social media account. With dNFTs, this NFT can change color, take on some kind of flair, or take on some other characteristic to show your ranking on the social media app, as evidenced by likes, reposts, comments, etc. This ” the ranking” could then theoretically unlock token-gated dAPPs, websites or digital experiences reserved for popular influencers.
Alternatively, this ranked dNFT can also be sold at a premium price versus an unranked version. Through NFT marketplaces, buyers and sellers will be able to trade these accounts with much greater fluidity than previously possible.
However, this capability is only one application. To fully understand the potential of dNFTs, one must first know how they work. Furthermore, how does Chainlink’s oracle technology help dynamic NFTs work? How do people even make dynamic NFTs? And overall, what are dynamic NFTs and how do dNFTs differ from traditional NFTs?
By reading this guide, you will gain an understanding of how dNFTs are already changing how we view and use NFTs. More importantly, we will also take a look at how dNFTs will have an even greater impact on our future.

Dynamic NFTs are a subcategory of NFTs coded with editable smart contract logic. This feature allows them to change their metadata based on external events. As a result of the metadata changing, the token itself also changes. This tool opens up a whole world of possible use cases that were previously impossible with traditional NFTs.

Like regular NFTs, dNFTS use blockchain technology to establish verifiable and immutable records of ownership and authenticity. When someone creates a dNFT, they set rules for how the NFT can be changed and which external events should be tracked. These rules are stored in the code itself.
Dynamic NFTs are transformed through the use of smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing programs that automate certain functions. They can be used to change the appearance or behavior of a dNFT depending on information received from an external oracle.
Oracles are hybrid smart contracts that connect blockchains to external systems. This connection allows an oracle smart contract to be executed based on real data. These oracles are key to allowing Web3 dApps and protocols to interact with legacy technology.
Oracles work by taking information from real APIs and then passing it to smart contracts. The smart contract then executes the programming and modifies the dNFT’s metadata. Changing the token’s metadata updates its properties and appearance.
In summary, dNFTs use oracles to ingest data from external sources. The oracle then interprets the data and dictates changes to dNFT’s metadata. Finally, the dNFT changes its appearance or behavior to adapt to the new information.
Traditional NFTs are static and cannot be changed once minted. Dynamic NFTs, on the other hand, are programmed to transform based on external inputs.
The differences between traditional NFTs and dynamic NFTs lend themselves to different use cases. Traditional NFTs are better suited for situations where the user prefers that the asset not change. This immutability provides increased security and safety – there is no chance of a traditional NFT changing after purchase.
This approach would be preferable for something like an alien CryptoPunk. A buyer wants the NFT based on its rarity and provenance, and definitely doesn’t want it altered at all.

Dynamic NFTs are a much better choice for more interactive projects. Using dNFTs for games, for example, would allow players to update characters after completing challenges. Basically, any scenario that would benefit from increased interactivity and flexibility would lend itself well to dNFTs.
Although dynamic NFTs are somewhat new, there have already been many projects using the technology.
Artblocks is a Web3 platform for generative art. Projects at Artblocks use dynamic NFTs to create generative pieces that exist at the intersection of computer programming and art. Many of these NFTs change over time, and rely on dynamic NFTs to make these transformations possible.
Like Artblocks, Async Art is a platform that helps artists create and collectors acquire programmable artwork. These elements adjust themselves based on external conditions using dynamic NFTs. This ability allows creators to create unique experiences in the chain for collectors.
Moonbirds has integrated dynamic NFTs into their 10k PFP project. Owners can stake their Moonbirds in a process called “nesting”. By doing so, they achieve different ranks that unlock rewards depending on how long they have been betting. The NFTs themselves also show different backgrounds depending on different things, for example how long they have been staked, whether the owner also has a valid passport, etc.
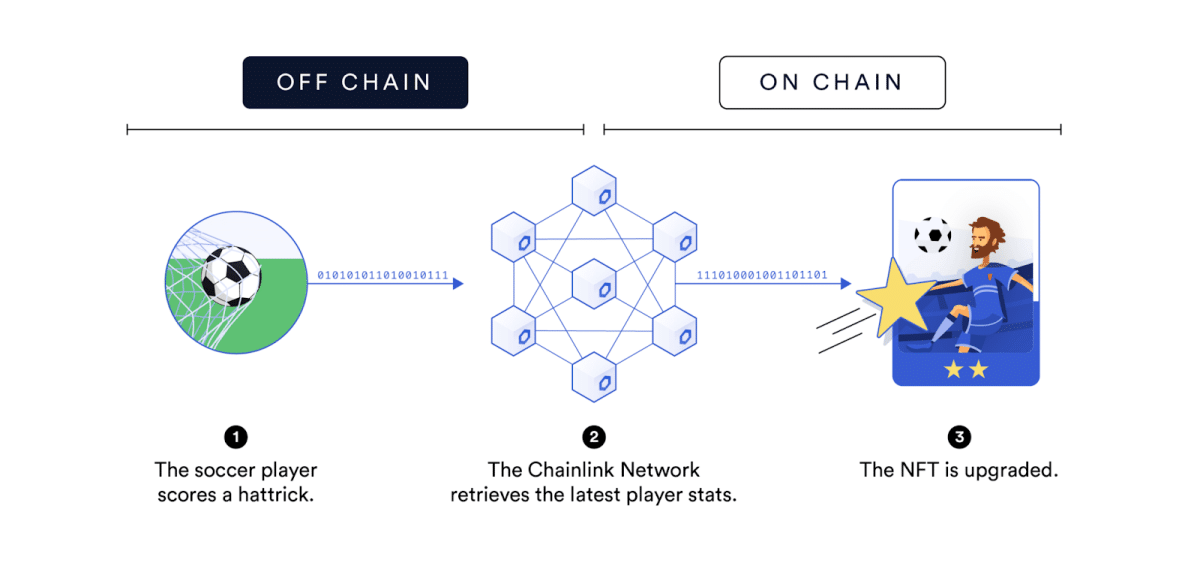
NBA star LaMelo Ball collaborated with Chainlink to release an innovative NFT collection based on dynamic NFT technology. The collection contains eight different NFT types, each version representing a specific statistic (points, rebounds, assists, etc.). Holders of the NFTs gained access to lottery tickets and other benefits depending on Ball’s performance on the field.
One type of LaMelo Ball NFT, The Gold Evolve NFT, promised to evolve into a new image if LaMelo won the Rookie of the Year award. The Charlotte Hornets player actually won the award, and as a result, the NFT transformed into a different image. To date, LaMelo Ball’s NFT collections are one of the greatest examples of what is possible when we begin to connect dynamic NFT technology to the world of digital collectibles.
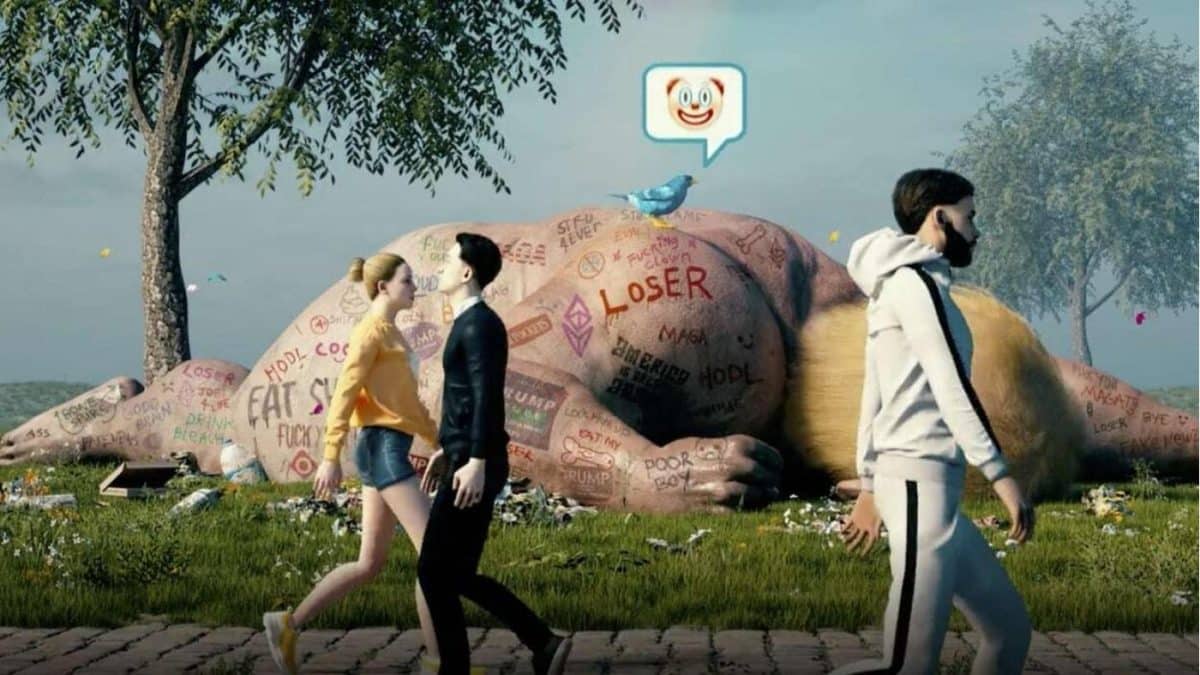
Beeple, otherwise known as Mike Winkleman, is helping to lead the early adoption of dynamic NFTs. Digital artist “Everydays” created a piece called “Crossroad” featuring Donald Trump. The play would either show a triumphant Donald Trump or a defeated Donald Trump based on the outcome of the 2020 presidential election.
As we all know, Trump lost the election. The NFT automatically updated to show a photo of the former president sprawled on the ground with “loser” graffitied on his naked body and a clown emoji floating over his body. The piece was so popular that it sold on the Nifty Gateway for $6.6 million.

However, dynamic NFTs can be used for much more than artwork. In fact, the vast majority of dNFTs will probably have nothing to do with art.
Gaming is perhaps the most obvious application for dynamic NFTs. For a long time, people have seen NFTs as a way to give players the ability to own hard-earned in-game assets without the interference of a centralized authority. Vitalik Buterin himself created Ethereum in response to Blizzard Entertainment screwing up his favorite World of Warcraft character. This experience led him to create Ethereum to allow greater decentralized ownership of digital assets.
With dynamic NFTs, players will be able to own NFTs that represent their characters and items. As these assets level up, their corresponding NFTs will also evolve to match their in-game performance. These items will be owned in individual owners’ wallets outside of the game publishers’ control. If a gaming company goes out of business, for example, the NFT will remain in a player’s wallet in addition to any game progress or achievements associated with it.
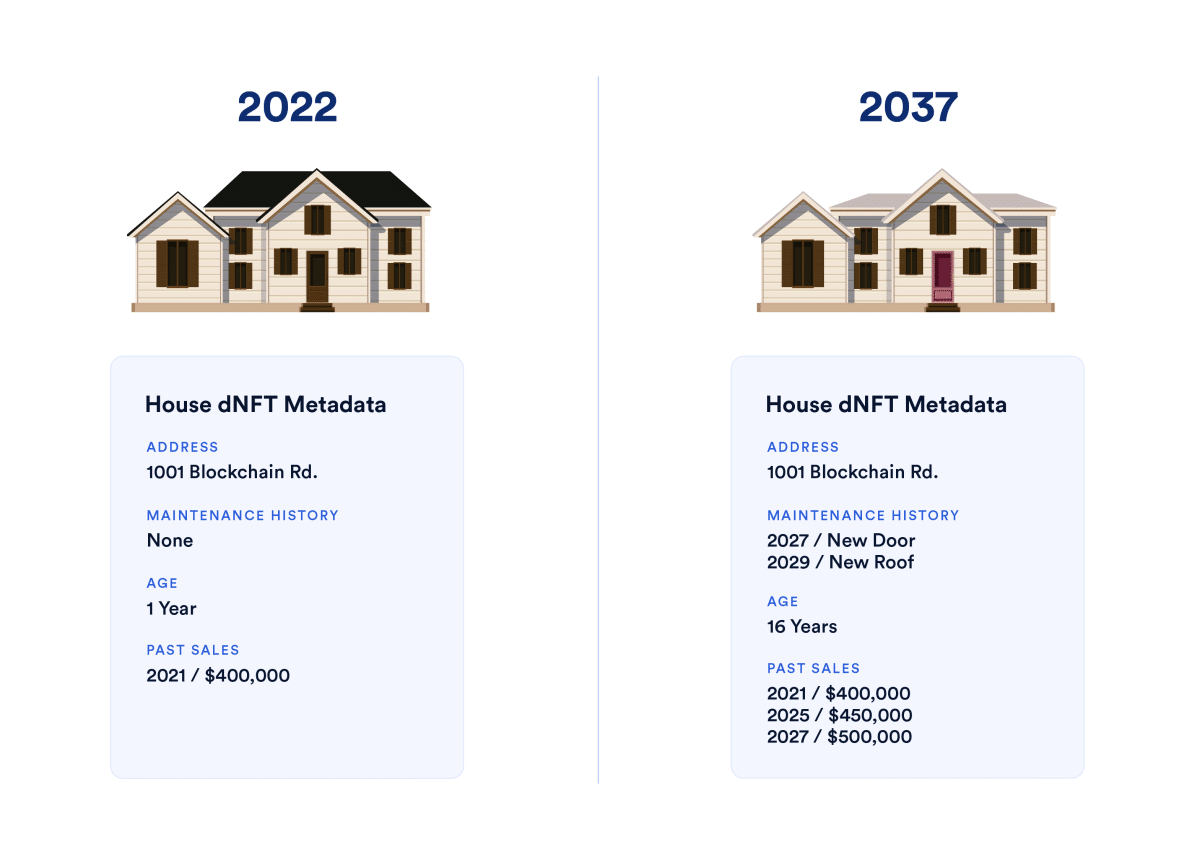
Real-world assets such as real estate will also be disrupted by dNFTs. Traditional property deeds, for example, may one day be replaced by dNFTs. When a property changes ownership, a dNFT will update itself to take the change into account.
Likewise, dNFTs can be used to represent homes themselves. The NFT can be updated when the property owner completes a major repair or upgrade. By doing so, we can create a simple solution for maintaining property records that are guaranteed to be accurate, transparent and accessible.
Dynamic NFTs also have an impact on fundraising. Regenerative Resources is an ecosystem services company using dNFTs to help plant 100 million mangroves. The organization produced the Five Short Film NFTs collection to fund this initiative. These NFTs reveal one frame of a short film each time one is bought or sold. This smart use of dNFTs is a great example of how this new blockchain technology is already improving our world.
Here are the steps to create a dynamic NFT:
We are only scratching the surface of what is possible with dynamic NFTs. The power to connect with the outside world will unleash enormous potential and bridge Web3 to everything that came before it. In all likelihood, dynamic NFTs will be so ubiquitous in our daily lives that we won’t even think of them as NFTs anymore.
As this trend continues, dynamic NFTs will become permanent elements of our daily lives and prove how important blockchain is to our future.
All investment/financial opinions expressed by NFTevening.com are not recommendations.
This article is educational material.
As always, do your own research before making any kind of investment.