Cosmos Hub drops ATOM 2.0 Whitepaper to bullish fanfare
Important takeaways
- Leading members of the Cosmos community shared their Cosmos Hub whitepaper today.
- The White Paper advocates reducing ATOM issuance to 0.1% and creating three major new structures for the Cosmos Hub.
- The proposed changes will likely make ATOM the Cosmos ecosystem’s reserve currency.
Share this article
Leading Cosmos figures want to introduce new tokenomics, an on-chain MEV marketplace, a system to streamline financial coordination across Cosmos blockchains, and a new governance structure for the Cosmos Hub.
ATOM 2.0 revealed
The Cosmos Hub is getting a serious makeover.
The long-awaited white paper for ATOM 2.0 was released today following a series of speeches by Cosmos co-founder Ethan Buchman, Osmosis co-founder Sunny Aggrawal, and Iqlusion co-founder Zaki Manian at Cosmoverse. The cosmos-centric event kicked off this morning in Medellín, Colombia, and will run through September 28.
The 27-page document, simply called ‘The Cosmos Hub’, was written by Buchman, Manian and eight other leading figures in the Cosmos community. Although it outlines new tokenomics for the Cosmos Hub’s token, ATOM, the paper is best known for proposing the implementation of several new features to the wider Cosmos ecosystem.
New ATOM Tokenomics
Cosmos is a decentralized network of independent blockchains. Not to be confused with the wider Cosmos ecosystem, the Cosmos Hub is a specific blockchain designed to connect all the other blockchains in the network. In its current form, ATOM’s main purpose is to provide security for the Cosmos Hub through a staking mechanism.
ATOM’s tokenomics have been criticized for their inflationary dynamics. ATOM issuance currently varies between 20% at worst and 7% at best, depending on the percentage of the total ATOM supply being staked. While total ATOM supply hovered of around 214 million in March 2019, data from CoinGecko indicates that over 292.5 million ATOM tokens are currently circulating – an increase of approximately 36.68%.
The white paper proposes a new monetary policy for ATOM, in two stages. A 36-month transition phase would first be introduced, at the beginning of which 10 million ATOMs would be issued per month (a short inflation rate increase of 41.03%, if launched today). The issuance rate would then level off to emissions of 300,000 ATOMs per month, effectively bringing ATOM’s inflation rate down to 0.1%.
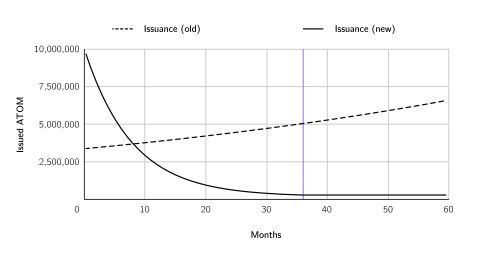
In the long term, ATOM issuance will therefore become linear rather than exponential.
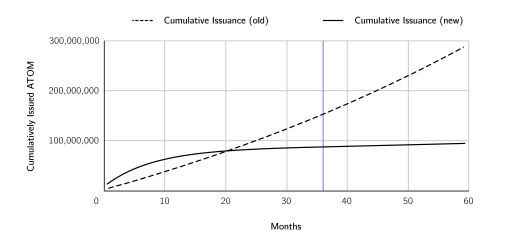
A main reason behind ATOM’s current monetary policy is to subsidize Cosmos Hub validators to provide security services. Under the new model, validators will instead be rewarded with the revenue generated by Interchain Security – a mechanism that allows the Cosmos Hub to produce blocks for other blockchains in the Cosmos ecosystem.
Interchain Security is expected to make building a Cosmos blockchain a faster, cheaper and easier process: it will also enable the creation of scaling solutions and increase overall IBC connectivity. A security mechanism will allow the original ATOM issuance model to be phased back in if Interchain Security revenue proves to be an insufficient substitute for validators.
Three new functions in Cosmos Hub
The white paper proposed the introduction of three main functions to the Cosmos Hub: Interchain Scheduler, Interchain Allocator and Governance Stack.
Interchain Scheduler
Interchain Scheduler will act as an MEV solution. MEV stands for “Maximal Extractable Value”, which refers to the profit that can be made by rearranging transactions within a block as it is being produced. Largely seen as inevitable, the practice has extracted more than $675 million from Ethereum users since January 2020. MEV mining has been streamlined on Ethereum through off-chain services such as Flashbots. Extractors (known as “seekers”) use these relays to negotiate with validators to implement their MEV strategies.
Cosmos Hub’s Interchain Scheduler intends to bring these negotiations on-chain and have the wider network benefit from them. A willing Cosmos blockchain can sell a portion of its block space to the Interchain Scheduler; the latter would then issue NFTs representing “block space reservations”. These tokens will be auctioned off periodically and possibly even traded on secondary markets. The original blockchain would then receive a portion of the revenue. According to the white paper, the Interchain Scheduler will complement (not replace) off-chain MEV relays, promote competition and decentralize the practice.
Interchain Allocator
The goal of the Interchain Allocator would be to streamline financial coordination across the Cosmos network. By establishing multilateral agreements between IBC blockchains and entities, the Allocator is expected to accelerate user and liquidity acquisition for Cosmos projects while securing ATOM’s position as the network’s reserve currency. Protocols can use the allocator for mutual ownership, expand ATOM’s liquid stake markets, rebalance reserves, or participate in another blockchain’s governance. It will also open up the possibility of creating Liquidity-as-a-Service providers, securing sub-collateralized financing practices and reducing the incidence of insolvency due to extreme market events.
According to the whitepaper, the liquidity unlocked by the Scheduler and Allocator will ultimately result in the Cosmos Hub having an “asymmetric advantage” against other liquidity providers in the Cosmos network: the blockchain will benefit from raising capital; providing capital will reduce security risk; it would therefore be able to add even more capital, and so on.
Governance Stack
Finally, the white paper advocated creating a governance superstructure for the entire Cosmos network, called the Governance Stack. Not unlike Allocator, Governance Stack’s mission will be to streamline governance throughout the cosmos by giving each blockchain a shared infrastructure and vocabulary.
This would possibly involve the creation of a Cosmos Hub Assembly, which would work together with councils made of DAOs from the IBC network. The assembly itself will be composed of representatives from each of these councils, with the number of seats representing the project’s weight in the ecosystem – a system already adopted by political structures such as the US Congress.
Final thoughts
Buchman and Manian emphasized during their presentations at Cosmoverse that the whitepaper was meant to be a conversation starter. Ultimately, the development of the Cosmos Hub will be up to ATOM holders, who can vote for or against any changes to the blockchain. While the proposal has only been up on the Cosmos Hub governance forum for a few hours, the response has been mostly positive so far.
Manian made little effort to hide his bullishness on stage, stating that Cosmos Hub’s new features would “make EIP-1559 look like a joke,” referring to Ethereum’s burning mechanism. He also titled his “$1K ATOM LFG.” ATOM is currently trade to $13.91, so such a run would represent a 7,089% price increase.
Should the Cosmos Hub DAO implement the features proposed by the whitepaper in some form (as it likely will), it will still take a minimum of three years for ATOM’s emissions to drop to 0.1%. However, there is little doubt that Cosmos Hub’s new features will increase the token’s utility and secure its position as the Cosmos ecosystem’s leading cryptocurrency.
Disclaimer: At the time of writing, the author of this piece owned BTC, ETH, ATOM and several other cryptocurrencies.


