What differentiates blockchain solutions from conventional record keeping solutions?
[gpt3]rewrite
Introduction to blockchain technology
In information technology, blockchain technology is a revolutionary innovation that promises to redefine the landscape of digital transactions and data management. This digital ledger technology leverages decentralization, cryptography, and immutable ledger properties that shape its unique aspects, distinguishing it from traditional databases and conventional record-keeping systems.
Decentralization and distributed networks
Unlike conventional record-keeping systems that are centralized and managed by a single authority, blockchain uses a distributed network of computers, known as nodes. This decentralization is the cornerstone of blockchain’s robust security features and peer-to-peer transactions. It eliminates the potential for data tampering, improves data protection and prevents the possibility of a single point of failure, creating a trustless system.
Cryptography and security
Blockchain technology uses advanced cryptographic hash functions that ensure data integrity and confidentiality. Each transaction in a blockchain is encrypted and linked to the previous one, adding an extra layer of security. This inherent encryption process in blockchain solutions improves data protection, a significant upgrade over conventional recording methods.
Immutable ledger and transparency
A prominent feature of the blockchain is its immutable ledger, which means that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be changed or deleted. This feature adds a superior level of data integrity compared to traditional databases. Furthermore, blockchain’s transparency ensures that all transactions can be traced back, which promotes accountability and trust in the system, thereby reducing the risk of fraud.
Verification process and consensus mechanisms
The verification process in the blockchain is managed through consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). These mechanisms ensure the authenticity of transactions, and offer a more secure verification process compared to conventional systems, which often involve central authorities or intermediaries.
Smart contracts and blockchain applications
Blockchain solutions also utilize smart contracts – self-executing contracts with terms of agreement written directly into lines of code. These allow for versatile blockchain applications in various sectors, including business, supply chain and financial services. Smart contracts streamline processes, increasing transaction speed and efficiency compared to conventional systems.

Interoperability and scalability
Interoperability is another important feature of blockchain solutions. Different blockchain networks can communicate and transact with each other, a factor that distinguishes them from isolated conventional systems. However, scalability remains a challenge for blockchain solutions. Despite the speed of transactions, the volume of data processed can sometimes create problems with scalability. Developers are continuously working to solve these challenges to ensure that blockchain solutions remain effective.
Public and private blockchains
There are two primary types of blockchains, public and private. Public blockchains are open to everyone and maintain the highest level of decentralization. Bitcoin is an example of a public blockchain. On the other hand, private blockchains, also known as permissioned blockchains, are restricted to certain members. They offer the benefits of blockchain while retaining some control over who can access the network.
Real-time verification
One of the critical advantages of blockchain solutions over traditional databases is the real-time verification feature. Once a transaction is initiated on the blockchain, it is verified almost immediately by nodes in the network. This real-time verification mechanism reduces processing time, making blockchain more efficient than traditional systems, which often require lengthy verification procedures.
Data storage
Blockchain has revolutionized data storage with its distributed ledger structure. Unlike conventional databases that store data in a central location, blockchain shares the data across multiple nodes in the network, creating a decentralized data storage system. This not only improves data security, but also ensures data redundancy and resilience against data loss.
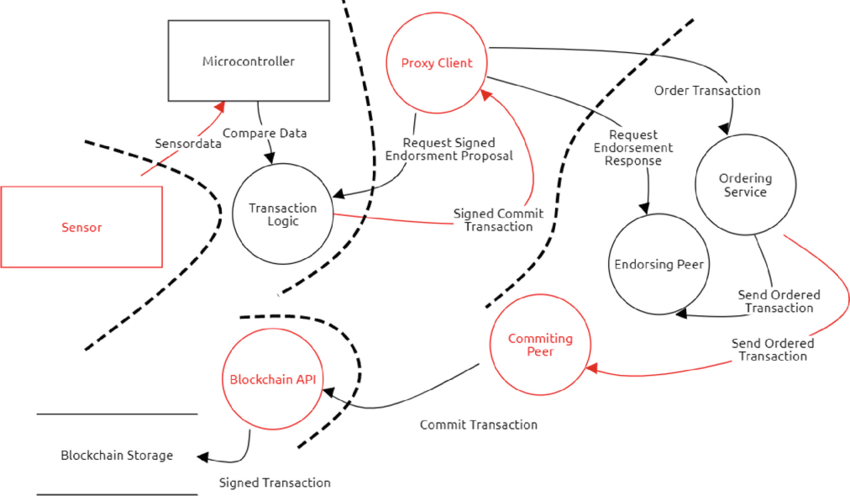
Transparency vs confidentiality
Transparency and confidentiality are two contrasting concepts in blockchain technology. Blockchain’s public ledger provides a high level of transparency, as every transaction can be traced back to its origin. However, blockchain also maintains confidentiality through the use of cryptographic techniques that ensure the identity of the parties involved. The balance between transparency and confidentiality distinguishes blockchain solutions from traditional record keeping systems.
Blockchain’s fundamental feature of disintermediation removes the need for intermediaries or central authority in transactions. This is in stark contrast to traditional systems that often require intermediaries for transaction validation. Through the use of smart contracts and consensus mechanisms, blockchain can validate and record transactions without third-party intervention, increasing efficiency and reducing costs.
Central authority in traditional systems
The role of a central authority is central to traditional databases. This authority maintains the system, validates transactions and controls access to information. However, central authority often leads to a single point of failure and risk of data manipulation. Blockchain solutions, by eliminating the need for a central authority, effectively solve these problems.
Prevention of fraud in blockchain
Blockchain’s immutable ledger, cryptographic security and decentralized nature make it highly resistant to fraud. Any attempt to change or delete a transaction is nearly impossible because it would require control of more than half of the network’s nodes. This inherent resistance to change significantly improves fraud prevention compared to conventional record keeping systems.
Traditional databases vs blockchain
Comparing traditional databases with blockchain highlights the revolutionary aspects of the latter. Where traditional databases are centralized, prone to data manipulation and dependent on intermediaries for transactions, blockchain is decentralized, secure, transparent and operates independently of intermediaries. These fundamental differences illustrate the disruptive potential of blockchain technology in various industry sectors.
Blockchain in Context: Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency
Bitcoin, the first application of blockchain technology, illustrates the potential of this decentralized model to manage digital assets securely and efficiently. Powered by blockchain, cryptocurrencies are disrupting the conventional financial landscape by removing middlemen, ensuring faster transactions and providing increased security.

Final thoughts: blockchain disruption
Blockchain technology is setting the stage for significant disruption in various industries. The security functions, decentralization and versatility provide a marked improvement compared to conventional record keeping solutions. Blockchain solutions offer not just an alternative, but an advanced and potentially superior method of managing digital transactions and data records. Although still in its developmental stages, there is no doubt that blockchain technology will continue to shape our digital future in unimaginable ways.
FAQ
Blockchain solutions offer a number of advantages over conventional record keeping systems. They provide enhanced security through cryptography, maintain data integrity with an immutable ledger, and eliminate a single point of failure in decentralization.
Decentralization refers to the storage of data over a network of computers instead of a central server. This makes it very difficult for hackers to compromise the data, providing superior security compared to conventional record keeping systems.
Blockchain maintains data integrity through an immutable ledger. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be changed or deleted. This ensures the accuracy and consistency of data throughout its lifecycle.
Traditional record keeping systems store data in a central location, which if compromised can lead to total system failure. In contrast, blockchain’s data is distributed across a network of computers, removing the single point of failure.
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into the code. They automatically execute transactions by meeting pre-defined criteria, eliminating the need for intermediaries and improving the efficiency of transactions.
Aside from cryptocurrencies, blockchain is used in various sectors including supply chain management, healthcare, finance and more. Its transparency, immutability and decentralization offer innovative solutions for data management and secure transactions in these fields.
While blockchain has many advantages, it also faces challenges such as scalability and energy consumption. Blockchain developers are constantly working to solve these problems and optimize the technology’s performance.
READ MORE:
How can functions in Blockchain support sustainability efforts
Xxc Renegade 1000 Xxc Price Prediction: Will This ATV Be Popular In 2023?
Reliance Power Stock Price Future Prediction 2025: Will RPOWER Stock Hit ₹100 in 2023?
Investing in Bitcoin: Unraveling the Complexity of GBTC Shares
Ja Bank share price prediction 2025: Will Ja Bank share recover from the crisis?
Checking Bitcoin Mining Hashrate: Report on Core Scientific 545M and Riot Blockchain 215M Earnings
Clear Stock Price Prediction 2025: Can LCID Shares Recover Amid Bearish Sentiment?
Understanding the IEX share price on the national exchange
[gpt3]


