All the advantages of Blockchain in logistics
The Blockchain In Logistics market size was valued at $3.3 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $1,620 billion by 2028 according to Verified Market Research, growing at a CAGR of 62.4% from 2021 to 2028.
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize logistics, providing a secure and efficient way to manage supply chain operations. By providing end-to-end visibility, blockchain can eliminate fraud, improve the quality and safety of products, streamline verification processes, reduce paperwork and enable better traceability.
There are many potential use cases for blockchain in logistics, including document verification, product authentication, smart contracts, asset tracking and digital identity management. With blockchain technology paving the way for improved efficiency and security in logistics operations, it is sure to lead to profound changes in the industry.
Advantages of Blockchain in logistics
Improved transparency
One of thThe main benefits of blockchain in logistics are the increased transparency it provides, providing a clear audit trail. This is possible because blockchain makes it possible to create fraud-proof digital documents called verifiable identification which can be instantly checked for authenticity in seconds. This makes it easier for supply chain managers to track the movement of goods, from production to delivery and identify any bottlenecks or delays in the process.
Improved efficiency
Logistics operations can be much more efficient when verifiable credentials are issued in organizations’ systems. Their instantly verifiable nature streamlines processes, reduces paperwork and minimizes errors. By automating tasks such as document verification, blockchain can reduce the time and cost of manual processes. This can result in faster and more accurate transactions, reduced lead times and improved customer satisfaction.
For example, blockchain can be used to automate customs clearance processes, reducing the time and cost of compliance checks. It can also help track shipments in real time, allowing logistics providers to optimize routes, reduce transit times and minimize the risk of delays or theft.
Better traceability
Traceability is a critical aspect of supply chain management, especially in industries such as food and pharmaceuticals, where safety and quality are essential. Blockchain can eliminate document fraud, help identify the origin of any quality problems, minimize the risk of counterfeiting and ensure that products meet regulatory standards.
For example blockchain can be used to verify the origin of organic products and ensure that the fish is sustainably sourced. Or in the event of a recall, blockchain can help identify the source of the problem and determine which products are affected. By offering end-to-end traceability, blockchain can improve the quality and safety of products and build trust with consumers, regulators and stakeholders.
Improved security
Blockchain provides security and enables data to be fraud-proof and immediately verifiable using cryptography. Cryptography is a broad term that refers to the practice of securing communications from third-party interference. It includes various techniques such as encryption and digital signatures. Cryptography ensures that the data in the document has not been tampered with since it was issued.
Blockchain Technology Basics
To further understand the potential and benefits of blockchain in logistics, it is important to understand the basics of how blockchain, decentralized identifiers (DID), and verifiable credential technologies work.
Blockchain
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions in a secure and transparent way. Instead of relying on a central authority to validate and authenticate transactions, blockchain uses a network of nodes to verify each transaction. Once confirmed, the transaction is added to the blockchain, forming a permanent and tamper-proof record.
Public Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) can be stored on the blockchain. For increased security and privacy, verifiable credentials linked to the DIDs are securely stored on user devices and not on the blockchain.
Verifiable Credentials (VCs)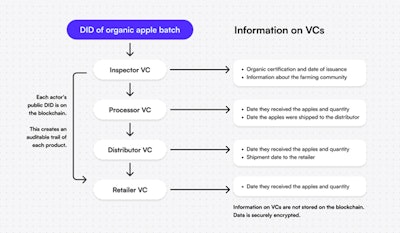 dock.io
dock.io
Verifiable identification is a new one way to securely store and share information about yourself, your products or your business. They are digital certificates that have been made fraud-proof and immediately verifiable using blockchain and cryptography.
In logistics, verifiable credentials can be used to improve supply chain transparency and efficiency. They offer a secure and flexible way to manage and share information in logistics, and help to streamline operations and increase trust among participants in the supply chain.
For example, a logistics company can issue verifiable credentials to its suppliers, which will provide proof that they comply with certain standards or regulations. These credentials can then be shared with other parties in the supply chain, such as customers or regulators, to ensure that the products are safe and meet the necessary requirements.
Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs)
A decentralized identifier (DID) is a way to identify something or someone without trusting someone central authority. A DID is like having a unique digital identification (similar to an ID number) that you control and can share with others. DIDs contain cryptographic keys that make a document fraud-proof and instantly verifiable. They enable organizations and individuals to manage, verify and protect their verifiable credentials and digital identity in a secure and efficient way.
In logistics, DIDs can be used to create a reliable, secure and efficient way to manage identities and data across the supply chain. Each party in a supply chain can have a DID such as the manufacturer, distributor, logistics company and so on. Each product can also have a DID to help track its movements.
Use cases for blockchain in logistics
Here are just a few of the many potential uses for blockchain in logistics:
- Instant Document Verification: Verifiable credentials enable instant document verification by allowing digital documents to be quickly and easily verified through the decentralized blockchain network. For example, the bill of lading will be issued as a verifiable credential that contains all the necessary information about the shipment, such as the departure date and the contents of the shipment, all of which is securely encrypted on the recipient’s individual devices, not on blockchain.
- Eliminating fraud: Blockchain, verifiable credentials and decentralized identifiers work together to provide a secure and tamper-proof system for identity and data verification. Organizations can ensure that the information they receive is accurate and reliable.
- Product authentication: Blockchain can be used to create a tamper-proof and immutable record of a product’s journey from producer to end consumer, allowing customers to verify the authenticity of the product and prevent the sale of counterfeit goods.
- Smart contracts: Blockchain can be used to automate certain processes in logistics, such as payments or contract enforcement, through the use of smart contracts. These contracts can be programmed to execute automatically when certain conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing costs.
- Digital identity: Blockchain can be used to create a decentralized and secure digital identity system for logistics participants, allowing them to veprovide their identity without relying on third-party intermediaries. This can help prevent fraud and improve security.
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize logistics operations by providing greater transparency, efficiency and security. By harnessing the power of distributed ledgers, decentralized identifiers (DIDs) and verifiable credentials, companies can gain visibility into their supply chains and automate certain processes. This can help reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, ensure compliance with regulations and increase safety in logistics operations.


