7 Ways Blockchain Technology Can Improve Carbon Trading Transparency
Carbon markets are expanding rapidly as nations, businesses and people struggle to meet their emission reduction targets. However, transparency is one of the challenges facing participants in the carbon markets. Blockchain technology can provide a solution by monitoring and reporting the trading of emission reductions, eliminating any double-counting problems, improving financial flows and helping to build trust. Despite being relatively new, blockchain technology can help address the challenges of transparency in carbon trading in the near future.
—
Increased net-zero commitments by individuals, businesses and governments have been accompanied by rapid growth in carbon trading. Carbon markets – which aims to reduce greenhouse gases (GHG) that contribute to global warming by allowing the purchase and sale of carbon credits – is expected to grow significantly, and the demand for carbon credits is expected to increase by more than 50 billion dollars by 2030. However, there are serious concerns about how carbon market trading is administered, including issues of trust, transparency and double-counting of reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. To address these challenges, a new digital technology known as blockchain has recently developed and is being used in carbon trading markets to improve and revolutionize the market structure by increasing transparency, lowering transaction costs and building trust. The technology allows resource transfers and transaction documentation via a secured and centralized database.
Alexandre Gellert Paristechnical officer at the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), stated that: “As countries, regions, cities and businesses work rapidly to implement the provisions of The Paris Agreementthey must use all innovative and state-of-the-art technologies available that can contribute to more stakeholder involvement, transparency and engagement and help build trust and promote innovative ideas in the fight against climate change, leading to improved climate action.”
Similarly, universities in Germany and Denmark have published one study outlines the potential benefits of blockchain technology in the development of an international carbon credit market. The report examines the viability of blockchain technology for a carbon market mechanism under Article 6.2 of the Paris Agreement.
You might also like: What are Carbon Credits?
What is Blockchain technology and how does it work?
The concept of “chained blocks” was originally proposed to solve the problem of double spending in Bitcoin; as a result, the term “blockchain” gradually became more generalized. Blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology that connects users online to produce a reliable transaction record without the need for a third party. It is a database that stores records, but unlike a regular database, a blockchain secures data in a way that makes system manipulation, tampering and forgery impossible.
In blockchain technology, the data is stored in “blocks”, which are then sequentially arranged and linked together to create an unbreakable chain. Each block in a chain consists of three basic components: data, a nonce (a 32-bit integer), and a hash (a 256-bit number concatenated with the nonce). The cryptographic hash is produced by a nonce at the beginning of a chain. Unless mined, the data in the block is considered signed and permanently bound to the nonce and hash.
When a transaction occurs, it is recorded as a “block” of data, and each block is linked to those that precede and follow it, forming an irrevocable chain referred to as a blockchain. Each additional block reinforces the previous block’s verification, and thus the entire blockchain. This makes the blockchain manipulative, and delivers the critical power of robustness.
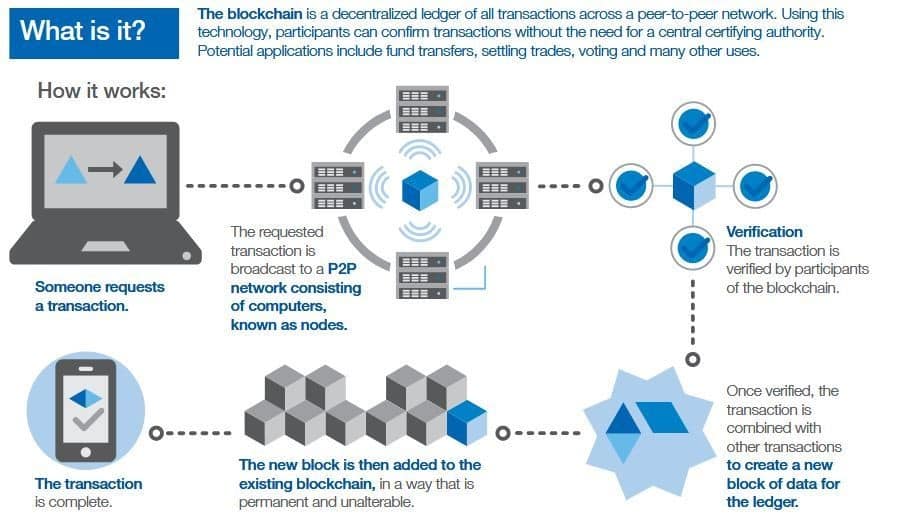
Picture 1: How blockchain technology works
How can blockchain technology improve transparency in carbon trading?
Carbon markets have traditionally been centralized, impenetrable and illiquid, resulting in very limited market participation. Blockchain has the potential to expand existing carbon markets and create new ones for a wider range of stakeholders, including small businesses and individuals. The technology records transactions publicly and permanently, helping to promote traceability and honesty.
Blockchain technology has the potential to improve carbon trading in the following ways:
1. Build consumer confidence and prevent greenwashing
One of the biggest challenges in trading carbon markets is the inaccuracy and unreliability of data. Many companies have fallen victim to greenwashing. Blockchain technology, however, offers a much more transparent and distributed method of keeping track of transactions, providing consumers with a detailed audit trail of all parts of a product at all stages of its life cycle.
2. Eliminate double counting
Blockchain has the potential to remove the possibility of duplicate counting – a situation where two parties demand the same emission reduction or carbon removal – and can enhance reliability, which reduces energy use and will attract participation from private finance, microfinance and crowdfunding.
3. Effective tracking of carbon markets
Blockchain can record a carbon credit’s complete journey, from creation through purchase to retirement. With the help of transparent credit tracking made easy by blockchain technology, voluntary markets can be expanded and made more accessible. The potential to aggregate small purchases via a transparent distributed ledger could help ordinary consumers reduce their environmental impact.
The technology can offer more transparency regarding the tracking of greenhouse gas emissions and make it easier to track and report emissions reductions, thereby addressing potential double-counting issues. It can serve as a tool to monitor the progress of the implementation Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement, as well as in company goals.
4. Streamline and accelerate carbon trading
Unlike either centralized or decentralized networks, the blockchain prevents monopolization of the system by eliminating the need for middlemen and enabling more streamlined and direct avenues for buying and selling credits. It can reduce the time required for clearance and trade approval by eliminating the requirement for intermediaries such as clearing houses. The use of smart contracts can speed up the buying and selling of carbon credits by digitizing the negotiation and agreement process.
5. Improve carbon emissions trading
Blockchain technology has the potential to improve the carbon asset trading system. Any credible information collected from a blockchain can help companies or organizations identify their problems and the reasons why they have not been environmentally friendly yet. As such, they will find it easier to define what being environmentally friendly means to them and to establish appropriate ways to achieve it.
6. Facilitate trade in clean energy and ensure proper use of funds
When it comes to finding accurate carbon credit information, such as validation and verification, there is a credibility issue. Blockchain technology can solve this by enabling the creation of systems for peer-to-peer trading of renewable energy. Consumers will be able to buy, sell or trade renewable energy with each other using tokens or tradable digital assets that represent a specific amount of energy production.
7. Improve climate finance flows
Blockchain technology has the ability to accelerate the development of crowdfunding and peer-to-peer financial transactions in support of climate action, while ensuring that funding is allocated to projects in a transparent manner. Blockchain will ensure that the revenue generated is solely used to address carbon emission issues and not to fund any alternative political agenda.
What is the current state of Blockchain technology in the carbon market?
The use of blockchain technology in carbon market trading is still relatively new, and many studies are being conducted around the world to determine the technology’s suitability for improving carbon trading. A 2022 study revealed that companies today are more willing to participate in carbon pilot projects using blockchain technology.
Another study identified 39 organizations developing blockchain solutions for carbon markets across two application areas: emissions trading schemes and voluntary carbon markets. Among them are IBM and Ben&Jerry’s, both of which recently partnered with blockchain companies to make carbon offsets more accessible to everyday consumers. IBM also collaborates with Veridium Labs to develop digital tokens to facilitate trading of carbon credits.
Poseidon is a pioneer in voluntary carbon markets, focusing on retail integration and attaching carbon credits to everyday purchases. CEO Laszlo Giricz explains: “When we realized that using Stellar blockchain transactions could be done in three seconds and at such a low cost, we realized that we could now trade in grams of carbon. Carbon credits can be incorporated into retail transactions at the point of sale for the first time.”
Other companies and organizations using or developing blockchain technology in their carbon credit trading include Climate trading, Air Carbon Exchange, Power ledger, Carbon only, Liquidity, Phaeton Blockchain, Carbonex, Blockchain for Climate Foundation.
Although blockchain technology is still in its infancy and early stages of development, it has the potential to be the best technology in the near future to address the challenges of transparency in carbon trading.
You might also like: Using blockchain technology in environmental protection


